Difference between revisions of "Debuggers"
From Genome Analysis Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
*:Set Breakpoint (can set properties – break after hit X number of times, etc) | *:Set Breakpoint (can set properties – break after hit X number of times, etc) | ||
:-or- | :-or- | ||
| − | * At the | + | * At the gdd prompt: |
*:<code>b <class>::<method></code> | *:<code>b <class>::<method></code> | ||
===== Attach to already running process ===== | ===== Attach to already running process ===== | ||
| − | *File->Attach to Process | + | * On the Menu Bar: |
| + | *: File->Attach to Process | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Run with options ===== | ||
| + | * At the gdb prompt run your program with options, replacing your executable name with "run": | ||
| + | *: <code>run <options></code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Backtrace (see where you are in execution, look up/down the call stack) ===== | ||
| + | * On the Menu Bar: | ||
| + | *: Status->Backtrace | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== See a variable's value ===== | ||
| + | * Right click the variable in the source code window and click “Print” (or to keep it tracked, click “Display”) | ||
| + | : -or- | ||
| + | * At the gdb prompt: | ||
| + | *: <code>p <variable></code> | ||
| + | * To Print in hex, At the gdb prompt: | ||
| + | *: <code>p/x <variable></code> | ||
Revision as of 12:17, 29 April 2011
Debuggers
Advantages/Disadvantages
- Advantages
- Single step through the code
- Stop execution at a given point to investigate where it goes and what the values are
- Attach to an already running program
- Disadvantages
- Not running real-time, so may not expose all problems
DDD
How to Compile for Debug
Compile with the option: -ggdb -O0
For the statgen library, you can compile with: make OPTFLAG="-ggdb -O0"
How to Start DDD
On a linux command line, type: ddd pathToYourExecutable/yourExecutable &
Do not specify command line options at this point. That will be done later when you type "run"
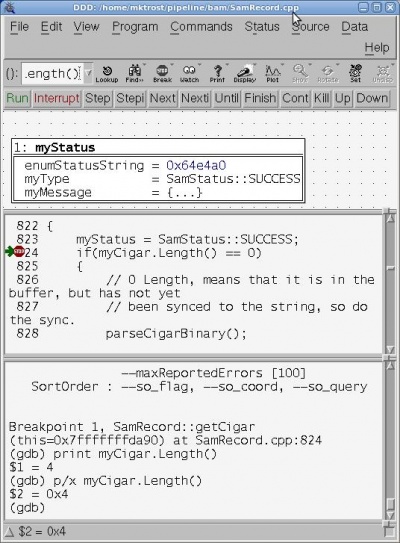
How to Use DDD
Debugging Tools
- Run: start the program with the previously specified options
- Interrupt: stop the program from running
- Step: Go into the function call (or go to next line of code)
- Next: Go over a function call (execute it, but do not step into it)
- Finish: Continue execution until the end of the current method
- Cont: Continue execution until the next breakpoint or the end of the program is reached.
- Kill: stop the program from running.
Basic Usage
Bring up a file in the viewer
- At the gdb prompt:
l <filename>:<line#>- -or -
l <class>::<method>
Examples:
l SamRecord.cpp:1l SamRecord::getCigar
Set a breakpoint
- Use mouse right-click on the line number
- Set Breakpoint (can set properties – break after hit X number of times, etc)
- -or-
- At the gdd prompt:
b <class>::<method>
Attach to already running process
- On the Menu Bar:
- File->Attach to Process
Run with options
- At the gdb prompt run your program with options, replacing your executable name with "run":
run <options>
Backtrace (see where you are in execution, look up/down the call stack)
- On the Menu Bar:
- Status->Backtrace
See a variable's value
- Right click the variable in the source code window and click “Print” (or to keep it tracked, click “Display”)
- -or-
- At the gdb prompt:
p <variable>
- To Print in hex, At the gdb prompt:
p/x <variable>