RAREMETALWORKER
RAREMETALWORKER is a tool for generating summary statistics for rare variants and gene level meta analyses using RAREMETAL.
If you feel this program is useful, please tell us your name and contact in this registration.
If you have any questions, please contact Shuang Feng sfengsph at umich dot edu or Goncalo Abecasis goncalo at umich dot edu.
Key Features
RAREMETALWORKER has the following features:
- Takes genotypes from either PED file or VCF file.
- Generates summary statistics for both related and unrelated individuals.
- Generates linkage disequilibrium matrices summarizing covariance between single marker statistics using an adjustable sliding window.
- Optionally handles related individuals using a kinship matrix derived from either pedigree or genotype data.
- Has the option of fitting shared environment.
- Can handle variants on Chromosome X.
- Calculates QC statistics such as hwe pvalue, call rate and genomic control.
- Automatically generate QQ and manhattan plots.
Software Download and Installation
Where to Download
- The source package for Linux can be downloaded here: RAREMTALWORKER
- The binary of RAREMETALWORKER can also be downloaded here: RAREMETALWORKER BINARY
- If you prefer to start from the source files, you can start from decompress the package using the following command:
tar xvzf Raremetalworker.0.4.3.tar.gz
- For UM CSG cluster users, no installation is needed. It is available at /net/fantasia/home/sfengsph/code/Rare-Metal/RareMetalWorker/bin/raremetalworker
How to Compile
- Go to /RareMetalWorker_0.4.3/RareMetalWorker/src and use the following command:
make
- If you prefer to use the binary file downloaded above, then no compiling is needed, but it is not guaranteed to work due to system and library requirements.
How to Execute
- To execute the program, go to /RareMetalWorker_0.4.3/RareMetalWorker/bin, then the program can be executed by ./raremetalworker.
- An example command line for a related sample when you have genotype info saved in VCF file is as following:
./raremetalworker --ped your.pheno.ped --dat your.pheno.dat --vcf your.geno.vcf.gz --prefix your.study
- An example command line for a related sample when you have genotype info saved in PED/DAT file is as following:
./raremetalworker --ped your.ped --dat your.dat --prefix your.study
- An example command line for an unrelated sample when you have genotype info saved in PED/DAT file is as following:
./raremetalworker --ped your.ped --dat your.dat --prefix your.study
- An example command line for an unrelated sample when you have genotype info saved in VCF file is as following:
./raremetalworker --ped your.pheno.ped --dat your.pheno.dat --vcf your.geno.vcf.gz --prefix your.study
- An example command line to use when you have genotype info saved in VCF file and you want to adjust covariates first and then inverse normalize residuals is as following:
./raremetalworker --ped your.pheno.ped --dat your.pheno.dat --vcf your.geno.vcf.gz --makeResiduals --inverseNormal --prefix your.study
- For more examples, please go to [Examples].
Software Specifications
Input Files
Rare-Metal-Worker needs the following files as input: PED and DAT file in Merlin format, AND/OR a VCF file. When genotypes are stored in PED and DAT file, the VCF file is not needed. However, even if genotypes are saved in a VCF file, PED and DAT files are still needed for carrying covariate and trait information.
PED and DAT Files
- When PED file has genotypes saved, there is no need for a VCF file as input.
- Rare-Metal-Worker takes PED/DAT file in Merlin format. Please refer to [PED/DAT format description] for details.
- An example PED file is in the following:
1 1 0 0 1 1.5 1 23 A A A A A A A A A A
2 1 0 0 1 1.0 1 34 A C A C A C A C A C
3 1 0 0 2 0.4 1 43 A A A A A A A A A A
4 1 0 0 2 0.9 1 13 A C A C A C A C A C
- The matching DAT file is in the following:
T YourTraitName C SEX C AGE M 1:123456 M 1:234567 M 2:111111 M 2:222222 M X:12345
- DAT file must have variant names in the following format "M chr:pos".
- Orders of labels in DAT file have to match the order of fields in PED file.
- Markers in PED and DAT file must be sorted by chromosome and position.
- Covariate and trait values are saved in PED file. Covariate and trait descriptions are saved in DAT file.
VCF File
- Another option is to use VCF as input. Please refer to the following link for VCF file specification: [1000 genome wiki VCF specs]
- VCF file should be compressed by bgzip and indexed by tabix, using the following command:
bgzip input.vcf ## this command will produce input.vcf.gz tabix -p vcf -f input.vcf.gz ## this command will produce input.vcf.gz.tbi
- Even with the presence of VCF file, PED/DAT files are still needed for covariates and phenotypes.
- Are you using PLINK file formats? Converting to VCF is easy. Use WDIST (very similar to PLINK) to make the conversion. Visit this page | WDIST to find documentation and downloads for WDIST.
Software Options
The following options are currently available in Rare-Metal-Worker:
Options:
Input Files : --ped [], --dat [], --vcf [], --dosage, --noeof
Output Files : --prefix [], --LDwindow [1000000], --zip, --thin,
--labelHits
VC Options : --vcX
Trait Options : --makeResiduals, --inverseNormal, --traitName []
Model Options : --recessive, --dominant
Kinship Source : --kinPedigree, --kinGeno, --kinFile [], --kinSave
Kinship Options : --kinMaf [0.05], --kinMiss [0.05]
Chromosome X : --xLabel [X], --xStart [2699520], --xEnd [154931044],
--maleLabel [1], --femaleLabel [2]
PhoneHome : --noPhoneHome, --phoneHomeThinning [100]
Input Files
- When genotypes are saved in a VCF file, PED and DAT files are used for specifying pedigree structure, covariate and trait information. An example command line might look like this:
--ped input.ped --dat input.dat --vcf input.vcf.gz
- When genotypes are saved in the PED file, the VCF file is not needed. An example command line might look like this:
--ped input.ped --dat input.dat
- If you want to analyze dosage data from VCF file, the following option has to be specified: --dosage. A key word "DS" in FORMAT field in VCF file has to included accordingly. An example is in the following:
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT T2DG1000582 ID1 ID2 ID3 22 16050408 37239779 T C . PASS AC=2;AN=496 GT:DS:GP ./.:.:0,0,0 ./.:.:0,0,0 ./.:.:0,0,0 22 16050933 37239784 G A . PASS AC=141;AN=904 GT:DS:GP 0/0:0.0:1,0,0 0/0:0.0:1,0,0 0/0:0.0:1,0,0
- --noeof allows using VCF file without BGZF EOF markers. This is a very rare option to use. If your run is terminated with error message: "", then you might want to check out this option.
Output Files
- --prefix is optional.
- If --prefix is not specified, the output file names will be:
traitname.singlevar.score.txt traitname.singlevar.cov.txt
- Otherwise, the output file names are:
prefix.traitname.singlevar.score.txt prefix.traitname.singlevar.cov.txt
- --LDwindow specifies the length of the window that LD Matrix should be generated upon each variant. The default is 1MB.
- --zip gives users the option of writing compressed files (bgzip compressed) automatically for convenient sharing.
- --thin tells RAREMETALWORKER to thin points when generating QQ plot and Manhattan plots, so the file size is smaller.
- --labelHits tells RAREMETALWORKER to to label the hits using pvalue threshold 0.05/(#of variants tested) with gene name, based on human genome build 19.
VC Options
- When --vcShared and --vcX are specified, Rare-Metal-Worker knows that you want to fit shared environment and/or chromosome X variance component together with genetic component and non-shared environment.
- When --makeResiduals is specified, Rare-Metal-Worker understands covariates should be read from PED/DAT file. Covariates are modeled as fixed effects.
Trait Options
- --makeResiduals tells RMW to adjust the covariates and analyze residuals instead of the original phenotypes. If either --kinGeno or --kinPedigree option is used, then a variance component model will be fit based on residuals. If the --inverseNormal option is also used, then the residuals will be quantile normalized before fitting variance component model.
- --traitName is created for situations when you have many traits saved in your PED and DAT file, but you are interested in one or a few of them. It can read a file ending with .txt with each trait of interest in a separate line, or trait names separated with "/". An example to handle one trait or multiple traits is in the following:
--traitName LDL --traitName LDL/HDL/TG --traitName traitsOfInterest.txt
- If --traitName is not used, all traits in PED/DAT file will be analyzed.
Model Options
- additive model is used in RMW as default.
- --recessive allows additional association results (pvalue, effect size, and standard error) generated using recessive model. If VCF file is used, then non-reference allele is considered the recessive allele. If PED/DAT files are used for genotype, then minor allele is considered the recessive allele.
- --dominant allows additional association results (pvalue, effect size, and standard error) generated using dominant model. If VCF file is used, then non-reference allele is considered the dominant allele. If PED/DAT files are used for genotype, then minor allele is considered the dominant allele.
- --recessive and --dominant options can be used together.
- Recessive and dominant results are stored in separate files.
Kinship Source
- --kinPedigree allows Rare-Metal-Worker to generate kinship matrix from pedigree, when pedigree information is available.
- --kinGeno informs Rare-Metal-Worker to generate kinship matrix from all available variants that pass the criteria, specified in --kinMaf and --kinMiss options. The default will take variants with MAF>0.05 and genotype missing rate <0.05.
- --kinGeno option can NOT be used with --kinPedigree or --kinFile option. Only one of three options or none of them can be used in the same run.
- --kinFile let Rare-Metal-Worker read in a kinship matrix from a file. The first row of the kinship file has to be the sample IDs included in the kinship file. If a sample of interest is not included in the kinship file, fatal error will occur and the program will be terminated. A sample of interest is a sample that is phenotyped and has all covariates measured when --makeResiduals is specified.
- --kinSave allows you to save the kinship matrix.
Kinship Options
- --kinMiss and --kinMaf should be used with --kinGeno together.
- --kinMiss specifies the maximum genotype missing rate when calculating kinship from genotypes. The default is 0.05.
- --kinMaf specifies the minimum minor allele frequency used when calculating kinship from genotypes. The default is 0.05.
Chromosome X
- --xLabel should have a value of a string which specifies how variants on chromosome X are coded. The default is "X".
- --xStart and --xEnd specifies the start and end of non-pseudo-autosomal regions on chromosome X. These options should be specified when --vcX is used.
- The default for --xStart is 2699520 and default for --xEnd is 154931044, according to NCBI genome build 37.
Please refer to the following for the analysis of X-linked variants ANALYZING CHROMOSOME X.
PhoneHome Parameters
See PhoneHome for more information on how PhoneHome works and what it does.
--noPhoneHomedisables PhoneHome. PhoneHome is enabled by default based on the thinning parameter.
--phoneHomeThinning(0-100) adjusts the frequency of PhoneHome.- By default,
--phoneHomeThinningis set to 50, running 50% of the time. - PhoneHome will only occur if the run's random number modulo 100 is less than the --phoneHomeThinning value.
- N/A if
--noPhoneHomeis set.
- By default,
- To let Rare-Metal-Worker handle unrelated individuals, we just have to code the individuals as unrelated in PED file, or each individual belongs to a unique family. Then Rare-Metal-Worker will take care of the rest.
- However, when --kinGenotype is also used, Rare-Metal-Worker will consider them as related and generate kinship matrix from genotypes.
- An example is shown as following (header is included for illustration purpose, not in real PED file):
famid pid fid mid sex age trait 1 1.1 0 0 1 10 -0.3 2 2.1 0 0 1 56 0.0 3 3.1 0 0 2 31 0.4 4 4.1 0 0 2 23 0.008 5 5.1 0 0 2 34 2.35
Output
- There are three files generated automatically by default:
prefix.traitName.singlevar.score.txt prefix.traitName.singlevar.cov.txt prefix.singlevar.log
- prefix.traitName.singlevar.score.txt contains summary statistics that are needed by Rare-Metal. An example is shown in below:
LDL mean= -0.00, variance= 1.00, heritability= 34.30 CHR POS REF_ALLELE ALT_ALLELE INFORMATIVE_N FOUNDER_AF ALL_AF INFORMATIVE_AC HWE_PVALUE STAT ALT_ALLELE_EFFSIZE PVALUE 10 45410002 G A 6103 0.0341589 0.0341589 410 0.165893 126.205 0.309798 4.03074e-10 19 45412079 G A 6103 0.0368124 0.0368124 434 0.714645 -265.84 -0.587356 7.87851e-36 19 45414451 G A 6103 0.444989 0.444989 5312 0.0759271 -26.1212 -0.00837122 0.640058
- pvalues from the above output are from the family-based single variant score test.
- prefix.traitName.singlevar.cov.txt contains the LD matrix among a variant and the adjacent markers within a prefixed-sized window. The default window size is 1MB. It has the following format:
CHR POS VAR_POS_IN_WINDOW LD_MATRIX 1 762320 762320,865628,865665,878744,879381,1560000 0.0359084,-0.000242112,-0.00125797,-0.000993422,-0.000344509,-0.00017077, 1 865628 865628,865665,878744,879381,1560000,1864659 0.419804,-0.0103663,-0.00635265,0.0594056,0.0534505,-0.00462183, 1 878744 878744,879381,1560000,1864659,1877659 0.000404537,-0.000235215,-1.4455e-05,-8.69137e-06,-3.1027e-05,
- RAREMETALWORKER generates QQ plot and Manhattan plots automatically. By using --labelHits option, users can choose whether to label the hits or not. Here is an example:
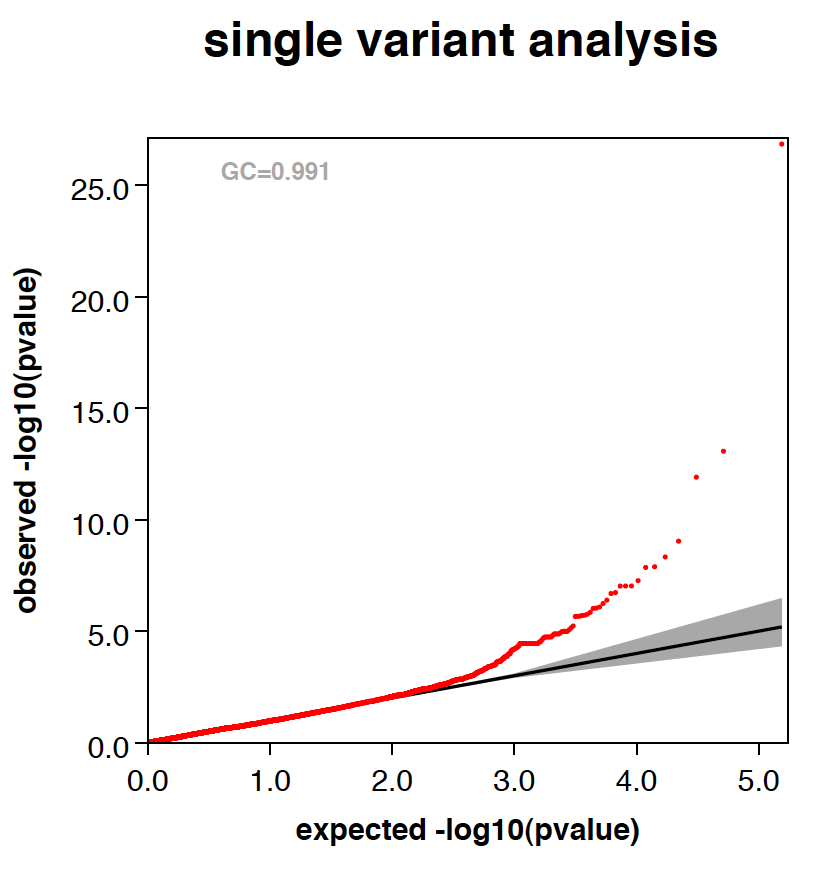
|
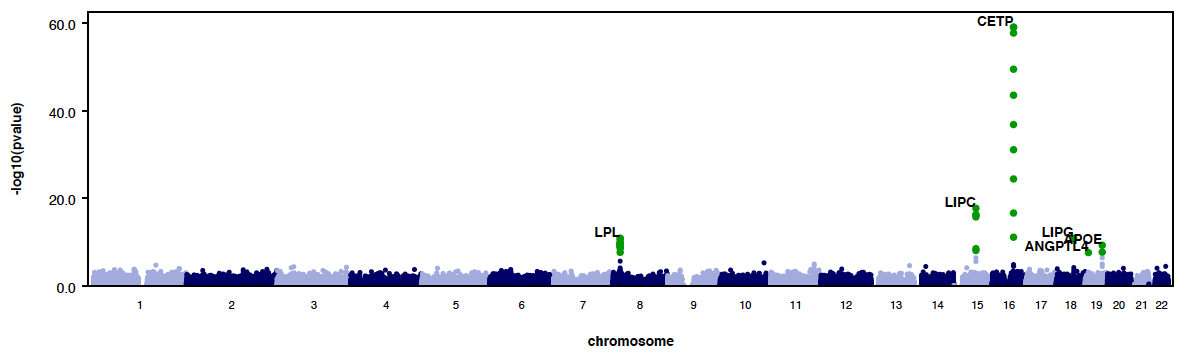
|
- RAREMETALWORKER generates a log file with options used:
Summary statistics for trait LDL have been saved in LDL.singlevar.score.txt. LD matrices for trait LDL have been saved in LDL.singlevar.cov.txt. Rare-Metal-Worker handled all individuals as related. The following parameters are in effect: Input Files: ============================ --ped [APOE.ped] --dat [APOE.dat] --vcf [] Output Files: ============================ --prefix [] --LDwindow [1000000] VC Options: ============================ --vcShared [false] --vcX [false] Trait Options: ============================ --makeResiduals [true] --inverseNormal [true] --traitName [LDL] Kinship Source: ============================ --kinPedigree [true] --kinGeno [false] --kinFile [] --kinSave [false] Kinship Options: ============================ --kinMaf [0.05] --kinMiss [0.05] Chromosome X: ============================ xLabel [X] xStart [2699520] xEnd [154931044]
Example Command Lines
Related individuals
- When you have genotype stored in ped file and dat file, and want to use pedigree kinship and inverse normalize trait values before adjusting any covariates and doing analysis:
/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --traitName LDL --inverseNormal --useCovariates
--labelHits (#this allows you to label the hits in manhattan plots.)
- When you have genotype stored in ped file and dat file, and want to use pedigree kinship and adjust covariates before inverse normalizing the residuals and doing further analysis:
/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --traitName LDL --useCovariates --makeResiduals --inverseNormal
- When you have genotype stored in ped file and dat file, and want to use kinship generated from genotypes:
/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --kinGeno --kinSave --traitName LDL
(#--kinSave allows you to save kinship matrix for future use; it is optional.)
- When you have genotype stored in vcf file and want to use pedigree kinship:
/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz
- When you have genotype stored in vcf file and want to use kinship generated from genotype:
/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --kinGeno --kinSave --labelHits
(#--kinSave allows you to save kinship matrix for future use.)
- Commands are the same as in above example, except each individual has to have a distinct family ID in PED file, and their father and mother ids should be "0".
- When you have genotypes from ped and marker information from dat file, and assuming no relatedness in the sample:
./raremetalworker --ped yours.ped --dat yours.dat --labelHits (#this allows you to label hits in manhattan plots.)
- When you have genotypes from vcf and covariates and trait information saved in ped and dat file, assuming there is no relatedness in the sample, you should use the following:
./raremetalworker --ped yours.ped --dat yours.dat --vcf yours.vcf.gz
- When you have genotypes from vcf and covariates and trait information saved in ped and dat file, assuming there is cryptic relatedness in the sample, you should use the following:
./raremetalworker --ped yours.ped --dat yours.dat --vcf yours.vcf.gz --kinGeno
(# -kinGeno handles individuals as related, and generate kinship matrix from genotype.)
Tutorial
- For a comprehensive tutorial of RareMetalWorker and RareMETAL using example data sets, please go to the following:
RAREMETAL and RAREMETALWORKER Tutorial
Q & A
Change Log
- Version 0.0.1 was released on 11/13/2012.
- Modified Rare-Metal-Worker to let it output LD matrix by a sliding window. (11/14/2012)
- Uploaded to public wiki. (11/16/2012)
- Enabled writing log file by defalut. (11/18/2012)
- Forced sample IDs to be matched when reading in kinship from a file. Perform a sanity check before reading in kinship file. If a sample of interest is not included in kinship file, then fatal error will occur. (11/19/2012)
- Added HWE pvalue and call rate in summary statistics output. (11/27/2012)
- Bugs fixed to solve compiling errors on some machines (Thank you Mary Kate!). Version 0.0.2 released. (11/30/2012)
- Updated output format. Version 0.0.3 released. (12/3/2012)
- More messages coded into log file. (12/4/2012)
- Version 0.0.4 released. (12/5/2012)
- Bug fixed for empirical kinship calculation when genotypes are read from VCF file. Version 0.0.5 released. (12/6/2012)
- Version 0.0.6 released. (12/6/2012)
- Updated output format for monomorphic sites. (12/7/2012)
- Changed executable name into bin/raremetalworker. Version 0.0.7 released. (12/10/2012)
- Fixed a bug when reading vcf file with ref or alt allele is missing. (2/5/2013)
- Fixed a bug when there is missing genotype from VCF file. (2/2013)
- Fixed a bug when handling chromosome X. Added sex labels option. (3/2/2013)
- Optimized code to speed up the process of calculating empirical kinship. (3/3/2013)
- Updated code to report allele frequencies calculated only from selected samples. (3/3/2013)
- Fixed bug in handling chromosome X. Added sanity checking steps before analysis. Added graphic support by generating QQ and manhattan plots automatically. Upgraded tool to version 2.8. (till 8/12/2013)
- Added support for analyzing dosages from VCF in version 2.9. (8/27/2013)
- Fixed the bug which causes crash when writing PDF when all variants are monomorphic. (10/6/2013)
- Fixed a few bugs handling chromosome X. Generated warning messages when male genotypes are coded wrong in VCF file. (11/25/2013)
- Released version 0.3.6 and fixed a minor bug that caused by code upgrades from version 0.3.5. (12/4/2013)
- Released version 0.3.7. Added dominant and recessive models as options. The default model is additive. (1/7/2014)
- Released version 0.4.0. Added phone home function. Saved Recessive and dominant results in separate files.
- Released version 0.4.1. Fixed a bug handling variants in nonPAR region on chromosome X when all samples are male.
- Released version 0.4.2. Fixed a bug that could possibly cause compiling error in some Linux system. Also, in this version, male heterozygous genotypes on chromosome X are considered missing. (3/10/2014)
- Released version 0.4.3. Fixed a few typo in messages. Added --noeof option for VCF files that does not have a BGZF EOF marker.