RAREMETALWORKER
RAREMETALWORKER is a tool for single variant analysis, generating summary statistics for gene level meta analyses in RAREMETAL.
If you feel this program is useful, please tell us your name and contact in this registration.
If you have any questions, please contact Sai Chen (saichen at umich dot edu) or Goncalo Abecasis (goncalo at umich dot edu).
Useful Wiki Pages
There are several pages in this Wiki that may be useful to RAREMETALWORKER users. Here are links to key pages:
- The RAREMETALWORKER command reference
- The RAREMETALWORKER method
- The RAREMETALWORKER quick start tutorial
- The RAREMETALWORKER special topics
- The RAREMETAL documentation
- The FAQ
- The Change Log
Key Features
RAREMETALWORKER has the following features:
- Takes genotypes from either PED file or VCF file.
- Generates summary statistics for both related and unrelated individuals.
- Generates linkage disequilibrium matrices summarizing covariance between single marker statistics using an adjustable sliding window.
- Optionally handles related individuals using a kinship matrix derived from either pedigree or genotype data.
- Has the option of fitting shared environment.
- Can handle variants on Chromosome X.
- Calculates QC statistics such as hwe pvalue, call rate and genomic control.
- Automatically generate QQ and manhattan plots.
Software Download and Installation
DOWNLOAD
We have tested compilation on several platforms including Linux, MAC OS X, and Windows.
For source code and executables together with instructions of building from source, please go to DOWNLOAD source and executables.
For questions about building and compilation, please go to FAQ.
How to Execute
- To execute the program, go to /RareMetalWorker_0.4.8/RareMetalWorker/bin, issue ./raremetalworker.
- For example command lines, please refer to RAREMETALWORKER EXAMPLES.
Method
Method description and key formulae can be found in RAREMETALWORKER METHOD.
For Binary Traits
RAREMETALWORKER currently treat all traits as quantitative. If your trait is binary, the odds ratio can be approximated from effect size estimates generated by RAREMETALWORKER. The installation/source package has a script included to augment the odds ratio estimates to the last column of the RAREMETALWORKER output. For details, please refer to Calculate Odds Ratio from RAREMETALWORKER output.
Software Specifications
INTERFACE
RAREMETALWORKER is a command line tool. Once you execute, you will see a full list of options printed on the screen.
For detailed description of command options, please go to command reference.
Options:
Input Files : --ped [], --dat [], --vcf [], --dosage, --noeof
Output Files : --prefix [], --LDwindow [1000000], --zip, --thin,
--labelHits
VC Options : --vcX, --separateX
Trait Options : --makeResiduals, --inverseNormal, --traitName []
Model Options : --recessive, --dominant
Kinship Source : --kinPedigree, --kinGeno, --kinFile [], --kinxFile [],
--kinSave
Kinship Options : --kinMaf [0.05], --kinMiss [0.05]
Chromosome X : --xLabel [X], --xStart [2699520], --xEnd [154931044],
--maleLabel [1], --femaleLabel [2]
others : --cpu [1], --kinOnly,
--geneMap [../data/refFlat_hg19.txt]
PhoneHome : --noPhoneHome, --phoneHomeThinning [100]
INPUT FILE FORMAT
RMW needs the following files as input: PED and DAT file in Merlin format, AND/OR a VCF file. When genotypes are stored in PED and DAT file, the VCF file is not needed. However, even if genotypes are saved in a VCF file, PED and DAT files are still needed for carrying covariate and trait information.
PED and DAT Files
- When PED file has genotypes saved, there is no need for a VCF file as input.
- RMW takes PED/DAT file in Merlin format. Please refer to PED/DAT format description for details.
- PED file requires "dummy" parents to be included in the pedigree file. To check the integrity of your PED/DAT file, please use pedstats. To add dummy parents into the pedigree, please use the perl script.
- An example PED file is in the following:
1 1 0 0 1 1.5 1 23 A A A A A A A A A A
2 1 0 0 1 1.0 1 34 A C A C A C A C A C
3 1 0 0 2 0.4 1 43 A A A A A A A A A A
4 1 0 0 2 0.9 1 13 A C A C A C A C A C
- The matching DAT file is in the following:
T YourTraitName C SEX C AGE M 1:123456 M 1:234567 M 2:111111 M 2:222222 M X:12345
- DAT file must have variant names in the following format "M chr:pos".
- Orders of labels in DAT file have to match the order of fields in PED file.
- Markers in PED and DAT file must be sorted by chromosome and position.
- Covariate and trait values are saved in PED file. Covariate and trait descriptions are saved in DAT file. Note that you must specify
--makeResidualsin order to adjust the covariates out of the phenotype. See Example Command Lines for examples and Trait Options for more information.
VCF File
GENOTYPES
- Another option is to use VCF as input. Please refer to the following link for VCF file specification: 1000 genome wiki VCF specs
- VCF file should be compressed by bgzip and indexed by tabix, using the following command:
bgzip input.vcf ## this command will produce input.vcf.gz tabix -p vcf -f input.vcf.gz ## this command will produce input.vcf.gz.tbi
- Even with the presence of VCF file, PED/DAT files are still needed for covariates and phenotypes.
- Are you using PLINK file formats? Converting to VCF is easy. Use WDIST (very similar to PLINK) to make the conversion. Visit this page | WDIST to find documentation and downloads for WDIST.
- When genotypes are saved in a VCF file, PED and DAT files are used for specifying pedigree structure, covariate and trait information. An example command line might look like this:
--ped input.ped --dat input.dat --vcf input.vcf.gz
- When genotypes are saved in the PED file, the VCF file is not needed. An example command line might look like this:
--ped input.ped --dat input.dat
DOSAGE
- If you want to analyze dosage data from VCF file, the following option has to be specified: --dosage. A key word "DS" in FORMAT field in VCF file has to included accordingly. An example is in the following:
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT IDx ID1 ID2 ID3 22 16050408 37239779 T C . PASS AC=2;AN=496 GT:DS:GP ./.:.:0,0,0 ./.:.:0,0,0 ./.:.:0,0,0 22 16050933 37239784 G A . PASS AC=141;AN=904 GT:DS:GP 0/0:0.0:1,0,0 0/0:0.0:1,0,0 0/0:0.0:1,0,0
- --noeof allows using VCF file without BGZF EOF markers. This is a very rare option to use. If your run is terminated with error message: "", then you might want to check out this option.
OUTPUT
OUTPUT FILE NAMES
- Three files are generated automatically by default:
prefix.traitName.singlevar.score.txt (single variant summary statistics and QC statistics) prefix.traitName.singlevar.cov.txt (covariance matrices of single variant score statistics) prefix.singlevar.log (log file)
- If --zip option is used, then the following will be generated automatically:
prefix.traitName.singlevar.score.txt.gz prefix.traitName.singlevar.score.txt.gz.tbi prefix.traitName.singlevar.cov.txt.gz prefix.traitName.singlevar.cov.txt.gz.tbi prefix.singlevar.log
- If --recessive and/or --dominant options are used, then the following files are also generated in addition to the above files
prefix.traitName.recessive.singlevar.score.txt.gz prefix.traitName.recessive.singlevar.cov.txt.gz prefix.traitName.dominant.singlevar.score.txt.gz prefix.traitName.dominant.singlevar.cov.txt.gz
- If --kinGeno --kinSave is used, then the genomic relationship matrix is stored in
prefix.Empirical.Kinship.gz
- If --vcX option is used, then the genomic relationship matrix from chromosome X is stored in
prefix.Empirical.KinshipX.gz
OUTPUT FILE FORMATS
Summary Statistics
- In the file with summary statistics named prefix.traitName.singlevar.score.txt contains summary statistics that are needed by Rare-Metal. An example is shown in below:
LDL mean= -0.00, variance= 1.00, heritability= 34.30 CHR POS REF_ALLELE ALT_ALLELE INFORMATIVE_N FOUNDER_AF ALL_AF INFORMATIVE_AC HWE_PVALUE STAT ALT_ALLELE_EFFSIZE PVALUE 10 45410002 G A 6103 0.034159 0.034159 410 0.165893 126.2050 0.309798 4.030740e-10 19 45412079 G A 6103 0.036812 0.036812 434 0.714645 -265.8400 -0.587356 7.878510e-36 19 45414451 G A 6103 0.444989 0.444989 5312 0.075927 -26.1212 -0.008371 6.400580e-01
- pvalues from the above output are from the family-based single variant score test.
LD Matrices
- prefix.traitName.singlevar.cov.txt contains the LD matrix among a variant and the adjacent markers within a prefixed-sized window. The default window size is 1MB. It has the following format:
CHR POS VAR_POS_IN_WINDOW LD_MATRIX 1 762320 762320,865628,865665,878744,879381,1560000 0.0359084,-0.000242112,-0.00125797,-0.000993422,-0.000344509,-0.00017077, 1 865628 865628,865665,878744,879381,1560000,1864659 0.419804,-0.0103663,-0.00635265,0.0594056,0.0534505,-0.00462183, 1 878744 878744,879381,1560000,1864659,1877659 0.000404537,-0.000235215,-1.4455e-05,-8.69137e-06,-3.1027e-05,
Genomic Relationship Matrix (GRM)
- Once --kinGeno --kinSave --prefix options are requested, you would expect to see a GRM generated (compressed by gzip) with name yourprefix.Empirical.Kinship.gz. If --prefix option is not used, then the file name is Empirical.Kinship.gz.
- If --vcX --kinGeno --kinSave --prefix options are requested, besides the autosomal GRM, you would also expect to see a separate GRM for chromosome X saved (compressed by gzip also) under the name yourprefix.Empirical.KinshipX.gz.
- The GRMs are generated based on all genotyped individuals included in the PED file; samples with missing phenotype or missing covariates are not excluded from GRMs. This feature makes GRMs reusable if you have multiple traits to analyze in separate runs. You can simplely use --kinFile option (--kinxFile option if you have X chromosome GRM together with --vcX option issued) to reuse the pre-saved GRMs.
- The format for both autosomal and chromosome X GRMs are the same. The first row has all sample IDs (sample size=N) listed. The rest of the file is a symmetric matrix with dimention NxN, and element ij of this matrix represents the kinship between the and the sample whose ID can be found from the first row.
- For details about GRM calculation, please refer to method.
Log File
- RMW automatically generates a log file named "yourprefix.singlevar.log".
- The first part of the log file has options used for your analysis saved.
The following parameters are in effect: Input Files: ============================ --ped [pheno.ped] --dat [pheno.dat] --vcf [allvars.vcf.gz] --dosage [false] --noeof [false] Output Files: ============================ --prefix [rmw.test] --LDwindow [1000000] --zip [false] --thin [false] --labelHits [false] VC Options: ============================ --vcX [true] --separateX [true] Trait Options: ============================ --makeResiduals [false] --inverseNormal [false] --traitName [] Model Options: ============================ --recessive [false] --dominant [false] Kinship Source: ============================ --kinPedigree [true] --kinGeno [false] --kinFile [] --kinxFile [] --kinSave [false] Kinship Options: ============================ --kinMaf [0.05] --kinMiss [0.05] Chromosome X: ============================ xLabel [X] xStart [2699520] xEnd [154931044] maleLabel [1] femaleLabel [2]
- The second part of the log file has all warnings and running messages saved.
Plots
- RAREMETALWORKER generates QQ plot and Manhattan plots automatically, unless there are only trivial number of variants analyzed.
- RAREMETALWORKER stores plots of each trait in separate files named yourprefix.traitname.plots.pdf.
- RAREMETALWORKER stores plots for recessive and dominant results separated with files named yourprefix.traitname.recessive.plots.pdf and yourprefix.traitname.dominant.plots.pdf.
- RAREMETALWORKER automatically generates three stratified QQ plots, one with all variants, one with variants of maf<0.05, and one with variants of maf<0.01.
- Genomic controls are automatically calculated and labeled in QQ plots.
- By using --labelHits option, users can choose to label the hits.
- Here is an example QQ plot and manhattan plot generated by RAREMETALWORKER.
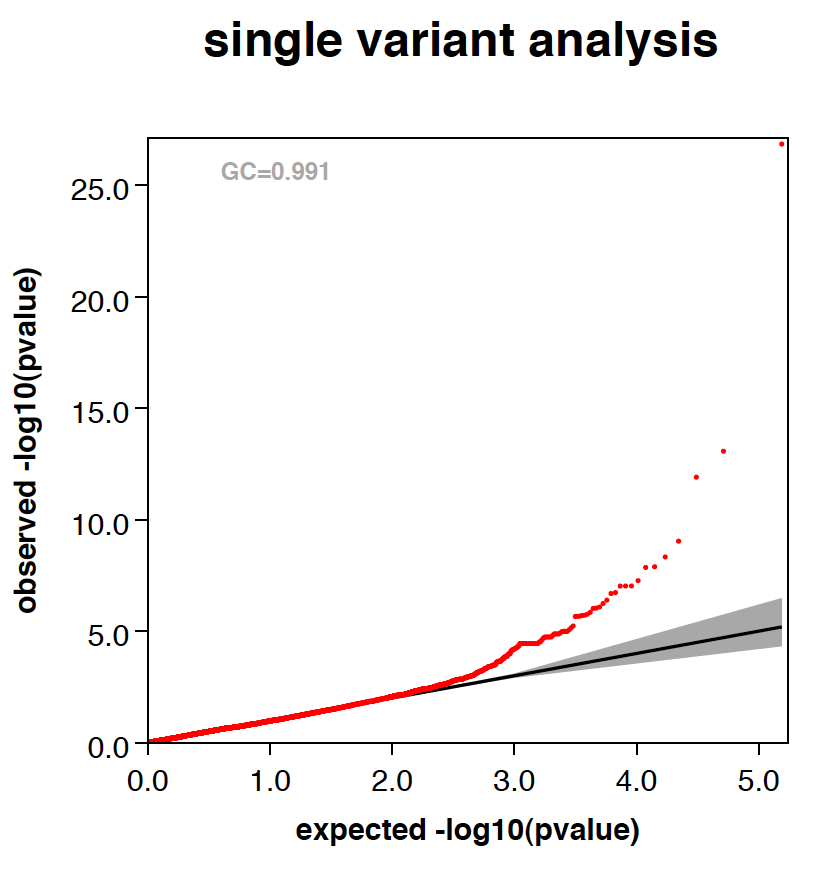
|
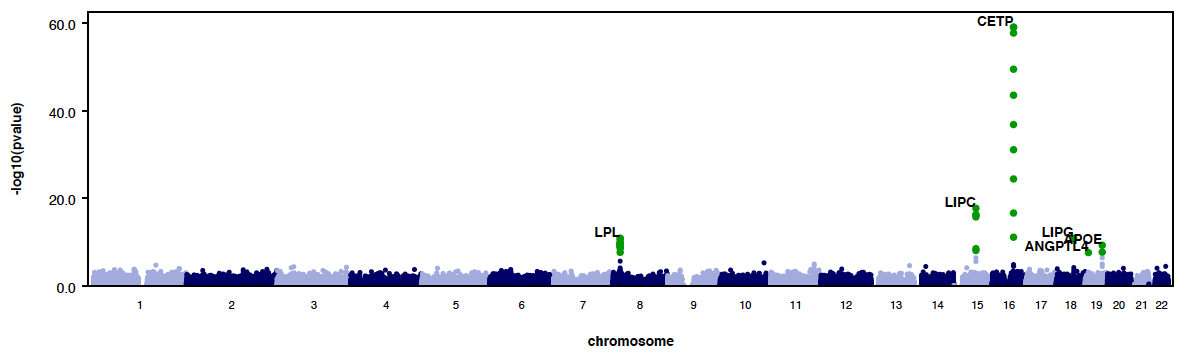
|
SPECIAL TOPICS
- For special topics such as how RAREMEALWORKER handles missing data, unrelated individuals, markers on chromosomeX, please go to SPECIAL TOPICS.
Example Command Lines
The following list a few popular combinations of options used for analyses. For an itemized description of options, please go to COMMAND REFERENCE.
General Usage
- If your PED file has many traits but you only want one of them to be analyzed, then the following command does the trick:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --traitName BMI --prefix yourFavoritePrefix
- If you want to inverse normalize (quantile normalize) your trait before doing associations, this can be done by adding --inverseNormal to your command line:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --traitName BMI --prefix yourFavoritePrefix --inverseNormal
- The following command will adjust covariates first and then use residuals to proceed association:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --traitName BMI --prefix yourFavoritePrefix --makeResiduals
- The following command will adjust covariates first and then use the inverse normalized residuals to proceed association:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --traitName BMI --prefix yourFavoritePrefix --makeResiduals --inverseNormal
Related individuals
- When pedigree is known and you want to use it to count for relatedness then the following command can be used:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --kinPedigree --prefix yourFavoritePrefix
- When you want to an estimated genomic relationship matrix to count for relatedness then the following command can be used:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --prefix yourFavoritePrefix --kinGeno --kinSave (this will save the genomic relationship matrix for future use)
- If the genomic relationship matrix has been saved previously, and you want to use it to count for relatedness then the following command can be used:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --prefix yourFavoritePrefix --kinFile yourPreviouslySavedKinship
- To analyze individuals as unrelated, even if pedigree is known, you just have to use the following command:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --prefix yourFavoritePrefix
Analyzing Chromosome X
- To analyze markers on chromosome X, if relatedness is not considered, then no special options needs to be issued.
- When relatedness is modeled using linear mixed model, and pedigree is known, then the following command fits use both autosomal kinship and chromosomeX kinship to fit a variance component model:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --kinPedigree --vcX --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --prefix yourFavoritePrefix
- Adding --separateX to the above command line will only use chromosome X kinship to fit the variance component model:
prompt> $PATH/bin/raremetalworker --ped yourInput.ped --dat yourInput.dat --kinPedigree --vcX --separateX --vcf yourInput.vcf.gz --prefix yourFavoritePrefix
- Please refer to METHODS for methods and SPECIAL TOPICS for technical details.
Using MERLIN format PED/DAT INPUT FILES
- When genotypes are stored in MERLIN format PED/DAT files, command should be the same to do the above analysis, except --vcf option should be excluded.
- Please refer to PED/DAT format for format requirements.
Tutorial
- For a comprehensive tutorial of RMW and RAREMETAL using example data sets, please go to the following:
RAREMETAL and RAREMETALWORKER Tutorial

