Difference between revisions of "SeqShop: Sequence Mapping and Assembly Practical, June 2014"
| (86 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | '''Note:''' the latest version of this practical is available at: [[SeqShop: Sequence Mapping and Assembly Practical]] | ||
| + | * The ones here is the original one from the June workshop (updated to be run from elsewhere) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
| + | See the [[Media:SeqShop - GotCloud Align.pdf|introductory slides]] for an intro to this tutorial. | ||
| + | |||
== Goals of This Session == | == Goals of This Session == | ||
* What we want to learn | * What we want to learn | ||
| Line 6: | Line 12: | ||
** How to visualize sequence data to examine the reads aligned to particular genomic positions | ** How to visualize sequence data to examine the reads aligned to particular genomic positions | ||
| + | == Setup in person at the SeqShop Workshop == | ||
| + | ''This section is specifically for the SeqShop Workshop computers.'' | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:600px"> | ||
| + | ''If you are not running during the SeqShop Workshop, please skip this section.'' | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{SeqShopLogin}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | === Setup your run environment=== |
| − | |||
| − | + | This will setup some environment variables to point you to | |
| − | * | + | * [[GotCloud]] program |
| + | * Tutorial input files | ||
| + | * Setup an output directory | ||
| + | source /home/mktrost/seqshop/setup.txt | ||
| + | * You won't see any output after running <code>source</code> | ||
| + | ** It silently sets up your environment | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:200px"> | ||
| + | View setup.txt | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | [[File:setup.png|500px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| − | + | == Setup when running on your own outside of the SeqShop Workshop == | |
| − | + | ''This section is specifically for running on your own outside of the SeqShop Workshop.'' | |
| − | * | + | <div class="mw-collapsible" style="width:600px"> |
| − | + | ''If you are running during the SeqShop Workshop, please skip this section.'' | |
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | === Download & Build GotCloud === | ||
| + | If you do not already have GotCloud: | ||
| + | * cd to where you want GotCloud installed (you can change this to any directory you want) | ||
| + | mkdir -p ~/seqshop | ||
| + | cd ~/seqshop/ | ||
| + | * download, decompress, and build the version of gotcloud that was tested with this tutorial: | ||
| + | wget https://github.com/statgen/gotcloud/archive/gotcloud.workshop.tar.gz | ||
| + | tar xvf gotcloud.workshop.tar.gz | ||
| + | mv gotcloud-gotcloud.workshop gotcloud | ||
| + | cd gotcloud/src | ||
| + | make | ||
| + | cd ../.. | ||
| − | + | Remember the path to gotcloud/ that is what you will need to set your GC variable to. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | === Download the example data === | |
| − | + | Download and untar file containing the example data used in the practicals: | |
| − | + | wget http://csg.sph.umich.edu//mktrost/seqshopExample.tar.gz | |
| + | tar xvf seqshopExample.tar.gz | ||
| − | + | You will see the names of all the files included in the example data scrolling on the screen as they are unpacked from the tar file. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{SeqShopRemoteEnv}} | |
| − | [[ | + | == Examining [[GotCloud]] Align Input Files == |
| + | === Examining Raw Sequence Reads : FASTQs === | ||
| + | FASTQ : standard file format provided to you by those who did the sequencing. | ||
| + | : For more information on the FASTQ format, see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FASTQ_format | ||
| − | + | For this tutorial, we will use FASTQs for 4 1000 Genome samples | |
| − | + | * Subset of FASTQs - should map to chromosome 22 36000000-37000000 | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ls ${SS}/fastq/ | ||
| + | There are 24 fastq files: combination of single-end & paired-end. | ||
| − | == | + | ;Can you tell which files are single-end and which are paired-end? |
| − | + | <ul> | |
| − | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:400px"> | |
| + | <li>View answer:</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li> Paired-end files have a '''_1.fastq''' or '''_2.fastq''' extension</li> | ||
| + | <li> This convention isn't mandatory, but something similar is common</li> | ||
| + | [[File:Fastqsm.png|700px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Look at a couple of FASTQs: | |
| + | less -S ${SS}/fastq/HG00551.SRR190851_1.fastq | ||
| + | <code>less</code> is a Linux command that allows you to look at a file. | ||
| + | *<code>-S</code> option prevents line wrap | ||
| + | * Use the arrow (up/down/left/right) keys to scroll through the file | ||
| + | * Use the <code>space bar</code> to jump down a page | ||
| + | Use <code>'q'</code> to exit out of <code>less</code> | ||
| + | q | ||
| − | [[File: | + | ;Do you remember the parts of a FASTQ? |
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:200px"> | ||
| + | <li>No, remind me:</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | [[File:Fastq.png|500px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| − | + | Look at the paired read: | |
| − | + | less -S ${SS}/fastq/HG00551.SRR190851_2.fastq | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Remember, use <code>'q'</code> to exit out of <code>less</code> | ||
| + | q | ||
| − | + | ;Do you notice something in common? | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <ul> | |
| − | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:400px"> | |
| − | [[File: | + | <li>View answer:</li> |
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li> Paired-end reads have matching read names with a different extensions</li> | ||
| + | <li> This convention isn't mandatory, but something similar is common</li> | ||
| + | [[File:Fastq3.png|500px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
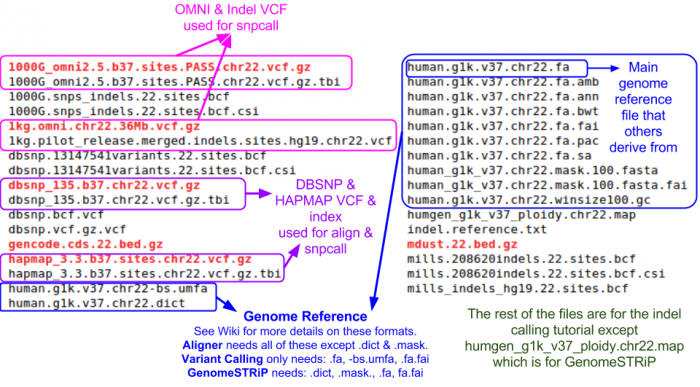
| − | See [[GotCloud: Genetic Reference and Resource Files]] for more information on downloading/generating reference files | + | === Reference Files === |
| + | Reference files can be downloaded with [[GotCloud]] or from other sources | ||
| + | * See [[GotCloud: Genetic Reference and Resource Files]] for more information on downloading/generating reference files | ||
| − | + | For alignment, you need: | |
| − | + | # Reference genome FASTA file | |
| + | #* Contains the reference base for each position of each chromosome | ||
| + | #* Additional information on the FASTA format: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FASTA_format | ||
| + | # VCF (variant call format) files with chromosomes/positions | ||
| + | #* dbsnp - used to skip known variants when recalibrating | ||
| + | #* hapmap - used for sample contamination/sample swap validation | ||
| − | + | Take a look at the chromosome 22 reference files included for this tutorial: | |
| − | + | ls ${SS}/ref22 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <ul> | |
| − | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:200px"> | |
| − | + | <li>View Screenshot</li> | |
| − | + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | |
| − | + | [[File:RefDir.png|700px]] | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | </ul> | |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Let's read the reference FASTA file (all reference bases for the chromosome): | ||
| + | less ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa | ||
| − | + | Remember, use <code>'q'</code> to exit out of <code>less</code> | |
| − | + | q | |
| − | + | ; Where is the reference sequence? | |
| − | + | <ul> | |
| − | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:500px"> | |
| − | + | <li>Answer:</li> | |
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>The ends of a chromosome are 'N' - unknown bases</li> | ||
| + | <li>Let's look at 5 lines of the file starting at line 300,000</li> | ||
| + | tail -n+300000 ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa |head -n 5 | ||
| + | [[File:Fasta.png|500px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| − | If you | + | If you want to access the FASTA file by position, you can use <code>samtools faidx</code> command |
| − | + | ${GC}/bin/samtools faidx ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa 22:36000000 | less | |
| − | + | or | |
| + | ${GC}/bin/samtools faidx ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa 22:36000000-36000100 | ||
| − | + | === GotCloud FASTQ Index File === | |
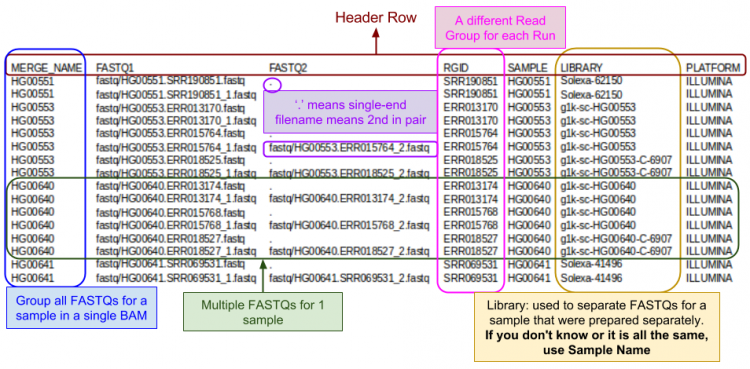
| − | + | The FASTQ index file is created by you to tell GotCloud about each of your FASTQ files: | |
| − | + | * Where to find it | |
| − | + | * Sample name | |
| − | + | ** Each sample can have multiple FASTQs | |
| − | + | ** Each FASTQ is for a single sample | |
| − | + | * Run identifier | |
| − | + | ** For recalibration we need to know which reads were in the same run. | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | FASTQ Index Format: | |
| + | * Tab delimited | ||
| + | * Starts with a header line | ||
| + | * One line per single-end read | ||
| + | * One line per paired-end read (only 1 line per pair). | ||
| − | + | Let's look a look at the index file I prepared for this tutorial: | |
| − | less -S ${ | + | less -S ${SS}/align.index |
| − | + | Remember, use <code>'q'</code> to exit out of <code>less</code> | |
| − | + | q | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
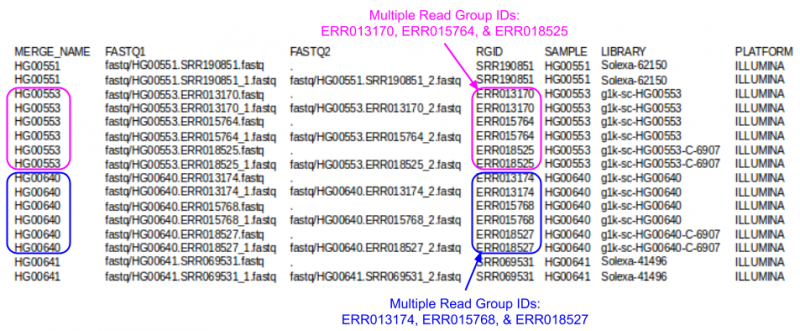
| − | + | ; Which samples had multiple runs? | |
| − | + | <ul> | |
| − | [[File: | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:500px"> |
| + | <li>Need a reminder of the format?</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | [[File:fqindex.png|750px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>Note: in the screenshots, the fields are shifted into clear columns to make it easier to read</li> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>When you view the file, the fields will not line up in neat columns and it can be hard to read</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:500px"> | ||
| + | <li>Hard to read the index? Need a hint?</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>Use cut to extract just the MERGE_NAME & RGID fields </li> | ||
| + | cut -f 1,4 ${SS}/align.index | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:500px"> | ||
| + | <li>Answer:</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>HG00553 & HG00640</li> | ||
| + | <li>They have multiple unique values in the RGID field</li> | ||
| + | [[File:fqindexRG.png|800px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | How do you point GotCloud to your index file? | |
| + | * Command-line <code>--index_file</code> option | ||
| + | : or | ||
| + | * Configuration file <code>INDEX_FILE</code> setting. | ||
The command-line setting takes precedence over the configuration file setting. | The command-line setting takes precedence over the configuration file setting. | ||
| − | + | === GotCloud Configuration File === | |
This file is created by you to configure GotCloud for your data. | This file is created by you to configure GotCloud for your data. | ||
| − | * Default values are provided in ${GC} | + | * Default values are provided in ${GC}/bin/gotcloudDefaults.conf |
** Most values should be left as the defaults | ** Most values should be left as the defaults | ||
* Specify values in your configuration file as: | * Specify values in your configuration file as: | ||
| − | + | ** <code>KEY = value</code> | |
* Use $(KEY) to refer to another key's value | * Use $(KEY) to refer to another key's value | ||
* If a KEY is specified twice, the later value is used | * If a KEY is specified twice, the later value is used | ||
* Does not have access to environment variables | * Does not have access to environment variables | ||
* '#' indicates a comment | * '#' indicates a comment | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Let's look at the configuration file I created for this test: | Let's look at the configuration file I created for this test: | ||
| − | more ${ | + | more ${SS}/gotcloud.conf |
| + | |||
| + | Use the <code>space bar</code> to advance if the whole file isn't displayed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; If your references are in a different path than what is specified, what would you change? | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:300px"> | ||
| + | <li>Answer:</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>You would change <code>REF_DIR</code> to the new path</li> | ||
| + | [[File:gcConf.png|800px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
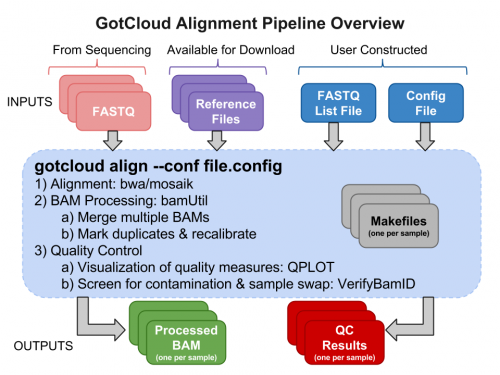
| + | == Run [[GotCloud]] Align == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:AlignDiagram.png|500px]] | ||
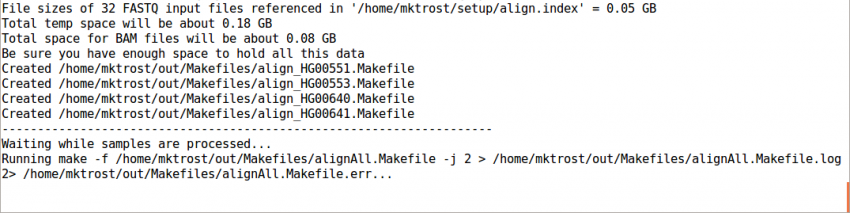
| − | + | Now that we have all of our input files, we need just a simple command to run them | |
| + | ${GC}/gotcloud align --conf ${SS}/gotcloud.conf --numcs 2 --base_prefix ${SS} --outdir ${OUT} | ||
| − | + | * <code>${GC}/gotcloud</code> runs GotCloud | |
| − | + | * <code>align</code> tells GotCloud you want to run the alignment pipeline. | |
| − | + | * <code>--conf</code> tells GotCloud the name of the configuration file to use. | |
| + | ** The configuration for this test was downloaded with the seqshop input files. | ||
* <code>--numcs</code> means to run 2 samples at a time. | * <code>--numcs</code> means to run 2 samples at a time. | ||
| − | ** | + | ** How many you can run concurrently depends on your system. |
| + | * <code>--base_prefix</code> tells GotCloud the prefix to append to relative paths. | ||
| + | ** The Configuration file cannot read environment variables, so we need to tell GotCloud the path to the input files, ${SS} | ||
| + | ** Alternatively, gotcloud.conf could be updated to specify the full paths | ||
| + | * <code>--out_dir</code> tells GotCloud where to write the output. | ||
| + | ** This could be specified in gotcloud.conf, but to allow you to use the ${OUT} to change the output location, it is specified on the command-line | ||
| + | |||
[[File:gcalignStart.png|850px]] | [[File:gcalignStart.png|850px]] | ||
| − | This should take | + | This should take 1-3 minutes to run. |
It should end with a line like: <code>Processing finished in 133 secs with no errors reported</code> | It should end with a line like: <code>Processing finished in 133 secs with no errors reported</code> | ||
| Line 256: | Line 306: | ||
If you cancelled GotCloud part way through, just rerun your GotCloud command and it will pick up where it left off. | If you cancelled GotCloud part way through, just rerun your GotCloud command and it will pick up where it left off. | ||
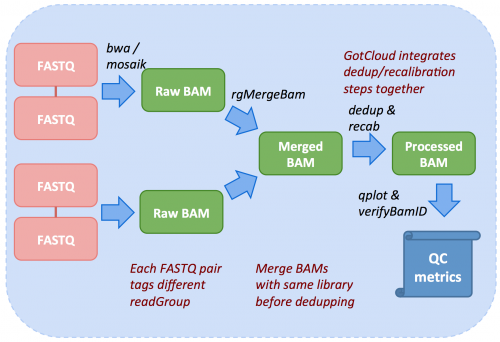
| − | + | Inside GotCloud align, not only sequence alignment but also pre-processing of sequence data, including deduplication and base quality recalibration are performed along with quality assessment, as illustrated below. | |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Gotcloud_align_detail.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Examining GotCloud Align Output == | ||
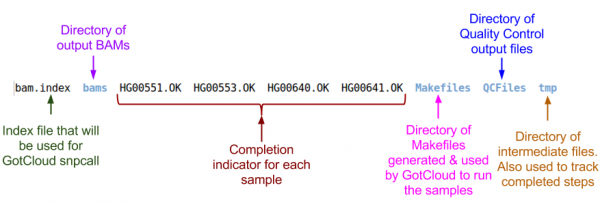
Let's look at the output directory: | Let's look at the output directory: | ||
| − | ls ${ | + | ls ${OUT} |
| − | [[File:gcalignOutM.png | + | [[File:gcalignOutM.png|600px]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
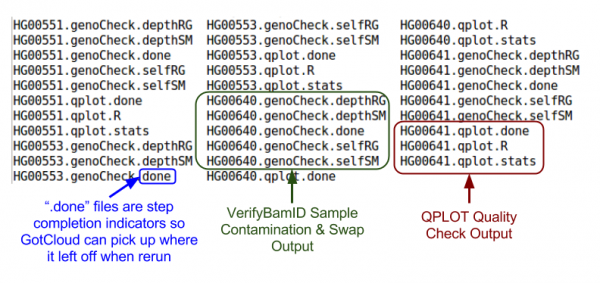
| + | === Quality Control Files === | ||
Let's take a look at our quality control output directory: | Let's take a look at our quality control output directory: | ||
| − | ls ${ | + | ls ${OUT}/QCFiles |
| − | [[File:GcalignOutQCm.png]] | + | [[File:GcalignOutQCm.png|600px]] |
| + | ==== Sample Contamination/Swap ==== | ||
Check for sample contamination: | Check for sample contamination: | ||
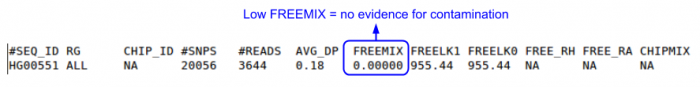
| + | * *.selfSM : Main output file containing the contamination estimate. | ||
| + | ** Check the 'FREEMIX' column for genotype-free estimate of contamination | ||
| + | **** 0-1 scale, the lower, the better | ||
| + | **** If [FREEMIX] >= 0.03 and [FREELK1]-[FREELK0] is large, possible contamination | ||
| + | ** See [[VerifyBamID#A_guideline_to_interpret_output_files|VerifyBamID: A guideline to interpret output files]] for more information | ||
| + | less -S ${OUT}/QCFiles/HG00551.genoCheck.selfSM | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remember, use <code>'q'</code> to exit out of <code>less</code> | ||
| + | q | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Is there evidence of sample contamination? | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:200px"> | ||
| + | <li>Answer:</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>No, FREEMIX = 0.00000 (<0.03)</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | [[File:Contam1.png|700px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== QC Metrics ==== | ||
| + | See: [[QPLOT#Diagnose_sequencing_quality|QPLOT: Diagnose sequencing quality]] for more info on how to use QPLOT results. | ||
| + | |||
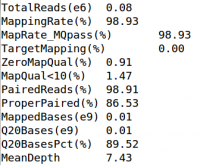
| + | Let's look at some quality control metrics: | ||
| + | cat ${OUT}/QCFiles/HG00551.qplot.stats | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; What is the mapping rate & average coverage for HG00551? | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:200px"> | ||
| + | <li>Answer</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li> 98.93% Mapped</li> | ||
| + | <li>7.43 MeanDepth</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | [[File:qplots.png|200px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Generate a pdf of quality metrics: | ||
| + | Rscript ${OUT}/QCFiles/HG00551.qplot.R | ||
| + | |||
| + | Examine the PDF: | ||
| + | evince ${OUT}/QCFiles/HG00551.qplot.pdf& | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is ok if you see a warning message when opening evince. It should still open. If not, let me know. To close evince, just close the pdf window. | ||
| + | |||
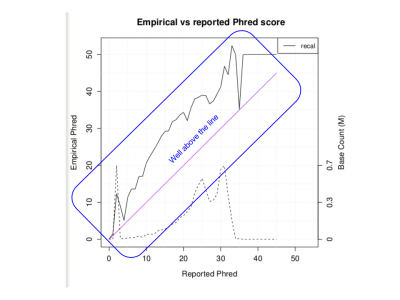
| + | ;Does the Empirical vs reported Phred score look as good as we would like? | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:400px"> | ||
| + | <li>Answer</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li> No, it is well above the line</li> | ||
| + | <li> This is due to the small region used for recalibration</li> | ||
| + | [[File:Qplotpdf.png|400px]] | ||
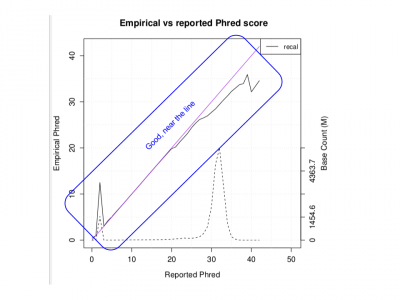
| + | <li> Look at the PDF I produced when I ran the whole genome:</li> | ||
| + | evince ${SS}/ext/HG00551.wg.qplot.pdf& | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | [[File:Qplotpdfwg.png|400px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === BAM Files === | ||
| + | Binary Sequence Alignment/Map (SAM) Format | ||
| + | * Maps reads to Chromosome/Position | ||
| + | * For a detailed explanation of the SAM/BAM format, see: | ||
| + | ** SAM/BAM Spec: http://samtools.github.io/hts-specs/SAMv1.pdf | ||
| + | ** Additional information I put together as I started working with SAM/BAM: [[SAM]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let's look at the BAMs (aligned reads that are ready for variant calling): | ||
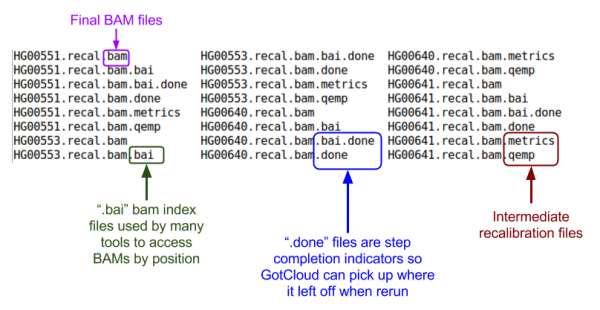
| + | ls ${OUT}/bams | ||
| + | [[File:GcalignOutBAMm.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
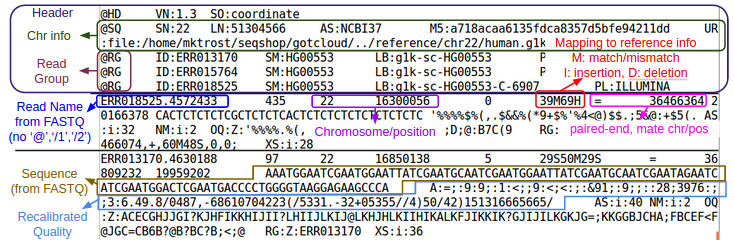
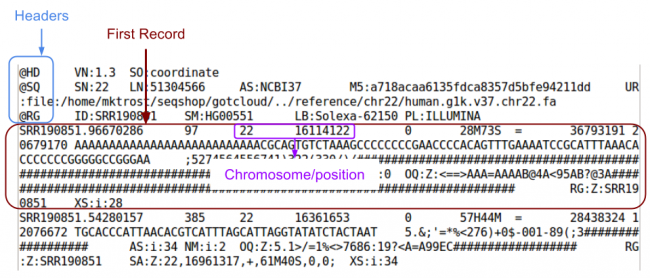
| + | Let's examine at the first 5 lines of the BAM file using [http://samtools.sourceforge.net/samtools.shtml#3 samtools view]: | ||
| + | ${GC}/bin/samtools view -h ${OUT}/bams/HG00551.recal.bam|head -n 5 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; What are the chromosome and position of the first record in the BAM file? | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:300px"> | ||
| + | <li>Need a reminder of the format?</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | [[File:Bam.png|750px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:300px"> | ||
| + | <li>Answer</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>Chr 22, Pos: 16114122</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | [[File:BamRec.png|650px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Accessing BAMs by Position ==== | ||
| + | BAM's are so big, what if we want to see a position part way through the file? | ||
| + | *[http://samtools.sourceforge.net/samtools.shtml#3 samtools] has an option for that. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add a region to the view command we used above. Let's find all reads that overlap positions 36907000-36907005: | ||
| + | ${GC}/bin/samtools view -h ${OUT}/bams/HG00551.recal.bam 22:36907000-36907005 | ||
| + | * Just a few reads. | ||
| + | |||
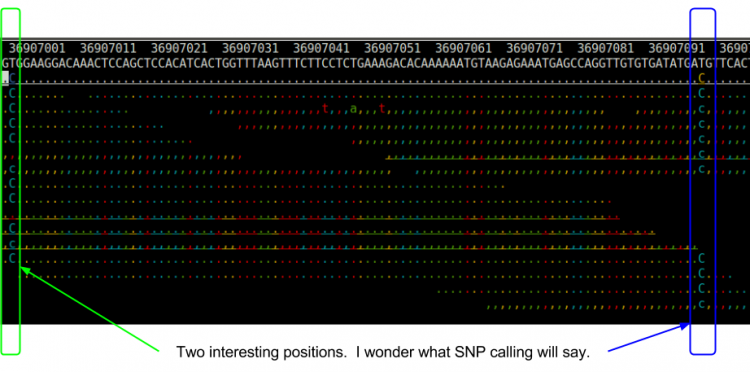
| + | Let's visualize what reads in that area look like using samtools tview: | ||
| + | ${GC}/bin/samtools tview ${OUT}/bams/HG00551.recal.bam ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa | ||
| + | * Type ‘g’ | ||
| + | ** Type 22:36907000 | ||
| + | * Type ‘n’ to color by nucleotide | ||
| + | * Use the arrow keys to move around and look at the area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Understanding the syntax: | ||
| + | * '.' : match to the reference on the forward strand | ||
| + | * ',' : match to the reference on the reverse strand | ||
| + | * ACGTN : mismatch to reference on the forward strand | ||
| + | * acgtn : mismatch to reference on the reverse strand | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Do you see anything interesting? | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:500px"> | ||
| + | <li>Screenshot</li> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>We will have to remember this region when we run snpcall to see what it says.</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | [[File:tview.png|750px]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other tview commands: | ||
| + | * Type '?' for a help screen | ||
| + | * Type 'q' to quit tview | ||
| + | |||
| + | Feel free to play around more and browse the BAM files. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Other tools for BAMs ==== | ||
| + | We have developed a lot of tools that operate on BAM files. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See [[Software#BAM_Util_Tools|Software: BamUtil Tools]] for a list | ||
| + | * Many operations: | ||
| + | ** diff : diff 2 BAM files | ||
| + | ** stats: per positions statistics | ||
| + | ** bam2Fastq : convert a BAM back to a FASTQ (how I created the fastqs for this tutorial) | ||
| + | ** Lots of others | ||
| + | * Feel free to try some out | ||
| + | * If you have any questions, let me know, I wrote most of them and am happy to help. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Logging Off == | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''This section is specifically for the SeqShop Workshop computers.'' | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:600px"> | ||
| + | ''If you are not running during the SeqShop Workshop, please skip this section.'' | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | To logout of seqshop-server, type: | ||
| + | exit | ||
| + | And close the windows. | ||
| − | + | When done, log out of the Windows machine. | |
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:07, 2 February 2017
Note: the latest version of this practical is available at: SeqShop: Sequence Mapping and Assembly Practical
- The ones here is the original one from the June workshop (updated to be run from elsewhere)
Introduction
See the introductory slides for an intro to this tutorial.
Goals of This Session
- What we want to learn
- Basic sequence data file formats (FASTQ, BAM)
- How to generate aligned sequences that are ready for variant calling from raw sequence reads
- How to evaluate the quality of sequence data
- How to visualize sequence data to examine the reads aligned to particular genomic positions
Setup in person at the SeqShop Workshop
This section is specifically for the SeqShop Workshop computers.
If you are not running during the SeqShop Workshop, please skip this section.
Login to the seqshop-server Linux Machine
This section will appear redundantly in each session. If you are already logged in or know how to log in to the server, please skip this section
- Login to the windows machine
- The username/password for the Windows machine should be written on the right-hand monitor
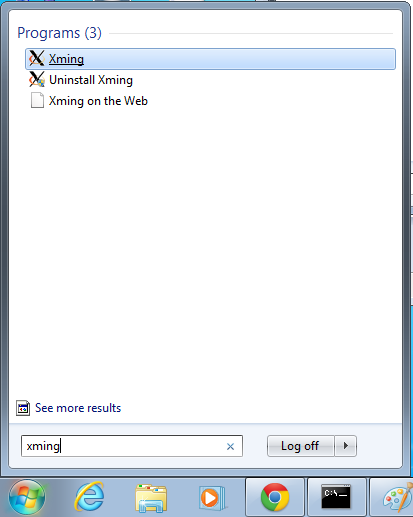
- Start xming so you can open external windows on our Linux machine
- Start->Enter "Xming" in the search and select "Xming" from the program list
- Nothing will happen, but Xming was started.
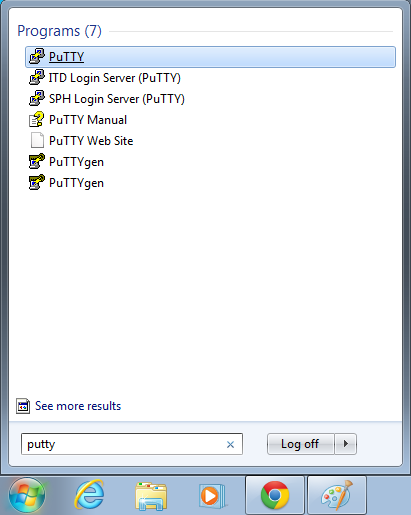
- Open putty
- Start->Enter "putty" in the search and select "PuTTY" from the program list
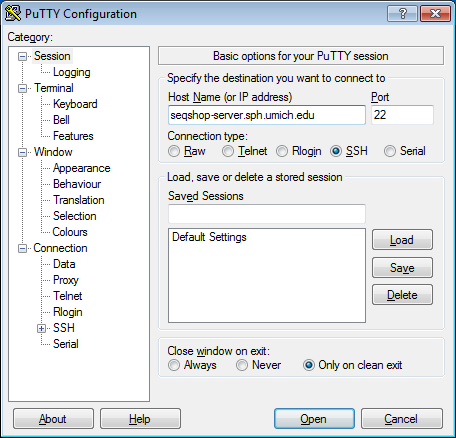
- Configure PuTTY in the PuTTY Configuration window
- Host Name:
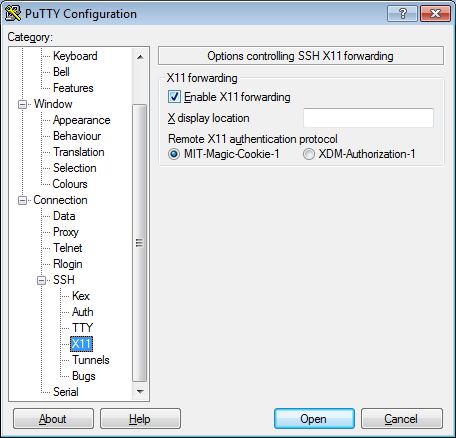
seqshop-server.sph.umich.edu - Setup to allow you to open external windows:
- In the left pannel: Connection->SSH->X11
- Add a check mark in the box next to
Enable X11 forwarding - Click
Open - If it prompts about a key, click
OK - Enter your provided username & password as provided
You should now be logged into a terminal on the seqshop-server and be able to access the test files.
- If you need another terminal, repeat from step 3.
Login to the seqshop Machine
So you can each run multiple jobs at once, we will have you run on 4 different machines within our seqshop setup.
- You can only access these machines after logging onto seqshop-server
3 users logon to:
ssh -X seqshop1
3 users logon to:
ssh -X seqshop2
2 users logon to:
ssh -X seqshop3
2 users logon to:
ssh -X seqshop4
Setup your run environment
This will setup some environment variables to point you to
- GotCloud program
- Tutorial input files
- Setup an output directory
source /home/mktrost/seqshop/setup.txt
- You won't see any output after running
source- It silently sets up your environment
Setup when running on your own outside of the SeqShop Workshop
This section is specifically for running on your own outside of the SeqShop Workshop.
If you are running during the SeqShop Workshop, please skip this section.
Download & Build GotCloud
If you do not already have GotCloud:
- cd to where you want GotCloud installed (you can change this to any directory you want)
mkdir -p ~/seqshop cd ~/seqshop/
- download, decompress, and build the version of gotcloud that was tested with this tutorial:
wget https://github.com/statgen/gotcloud/archive/gotcloud.workshop.tar.gz tar xvf gotcloud.workshop.tar.gz mv gotcloud-gotcloud.workshop gotcloud cd gotcloud/src make cd ../..
Remember the path to gotcloud/ that is what you will need to set your GC variable to.
Download the example data
Download and untar file containing the example data used in the practicals:
wget http://csg.sph.umich.edu//mktrost/seqshopExample.tar.gz tar xvf seqshopExample.tar.gz
You will see the names of all the files included in the example data scrolling on the screen as they are unpacked from the tar file.
Setup your run environment
Environment variables will be used throughout the tutorial.
We recommend that you setup these variables so you won't have to modify every command in the tutorial.
- Point to where you installed GotCloud
- Point to where you installed the seqshop files
- Point to where you want the output to go
- Using bash (replace the paths below with the appropriate paths):
export GC=~/seqshop/gotcloud export SS=~/seqshop/example export OUT=~/seqshop/output
- Using tcsh (replace the paths below with the appropriate paths):
setenv GC ~/seqshop/gotcloud setenv SS ~/seqshop/example setenv OUT ~/seqshop/output
Examining GotCloud Align Input Files
Examining Raw Sequence Reads : FASTQs
FASTQ : standard file format provided to you by those who did the sequencing.
- For more information on the FASTQ format, see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FASTQ_format
For this tutorial, we will use FASTQs for 4 1000 Genome samples
- Subset of FASTQs - should map to chromosome 22 36000000-37000000
ls ${SS}/fastq/
There are 24 fastq files: combination of single-end & paired-end.
- Can you tell which files are single-end and which are paired-end?
Look at a couple of FASTQs:
less -S ${SS}/fastq/HG00551.SRR190851_1.fastq
less is a Linux command that allows you to look at a file.
-Soption prevents line wrap- Use the arrow (up/down/left/right) keys to scroll through the file
- Use the
space barto jump down a page
Use 'q' to exit out of less
q
- Do you remember the parts of a FASTQ?
Look at the paired read:
less -S ${SS}/fastq/HG00551.SRR190851_2.fastq
Remember, use 'q' to exit out of less
q
- Do you notice something in common?
Reference Files
Reference files can be downloaded with GotCloud or from other sources
- See GotCloud: Genetic Reference and Resource Files for more information on downloading/generating reference files
For alignment, you need:
- Reference genome FASTA file
- Contains the reference base for each position of each chromosome
- Additional information on the FASTA format: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FASTA_format
- VCF (variant call format) files with chromosomes/positions
- dbsnp - used to skip known variants when recalibrating
- hapmap - used for sample contamination/sample swap validation
Take a look at the chromosome 22 reference files included for this tutorial:
ls ${SS}/ref22
Let's read the reference FASTA file (all reference bases for the chromosome):
less ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa
Remember, use 'q' to exit out of less
q
- Where is the reference sequence?
If you want to access the FASTA file by position, you can use samtools faidx command
${GC}/bin/samtools faidx ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa 22:36000000 | less
or
${GC}/bin/samtools faidx ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa 22:36000000-36000100
GotCloud FASTQ Index File
The FASTQ index file is created by you to tell GotCloud about each of your FASTQ files:
- Where to find it
- Sample name
- Each sample can have multiple FASTQs
- Each FASTQ is for a single sample
- Run identifier
- For recalibration we need to know which reads were in the same run.
FASTQ Index Format:
- Tab delimited
- Starts with a header line
- One line per single-end read
- One line per paired-end read (only 1 line per pair).
Let's look a look at the index file I prepared for this tutorial:
less -S ${SS}/align.index
Remember, use 'q' to exit out of less
q
- Which samples had multiple runs?
- Note: in the screenshots, the fields are shifted into clear columns to make it easier to read
- When you view the file, the fields will not line up in neat columns and it can be hard to read
- Hard to read the index? Need a hint?
- Use cut to extract just the MERGE_NAME & RGID fields cut -f 1,4 ${SS}/align.index
How do you point GotCloud to your index file?
- Command-line
--index_fileoption
- or
- Configuration file
INDEX_FILEsetting.
The command-line setting takes precedence over the configuration file setting.
GotCloud Configuration File
This file is created by you to configure GotCloud for your data.
- Default values are provided in ${GC}/bin/gotcloudDefaults.conf
- Most values should be left as the defaults
- Specify values in your configuration file as:
KEY = value
- Use $(KEY) to refer to another key's value
- If a KEY is specified twice, the later value is used
- Does not have access to environment variables
- '#' indicates a comment
Let's look at the configuration file I created for this test:
more ${SS}/gotcloud.conf
Use the space bar to advance if the whole file isn't displayed.
- If your references are in a different path than what is specified, what would you change?
Run GotCloud Align
Now that we have all of our input files, we need just a simple command to run them
${GC}/gotcloud align --conf ${SS}/gotcloud.conf --numcs 2 --base_prefix ${SS} --outdir ${OUT}
${GC}/gotcloudruns GotCloudaligntells GotCloud you want to run the alignment pipeline.--conftells GotCloud the name of the configuration file to use.- The configuration for this test was downloaded with the seqshop input files.
--numcsmeans to run 2 samples at a time.- How many you can run concurrently depends on your system.
--base_prefixtells GotCloud the prefix to append to relative paths.- The Configuration file cannot read environment variables, so we need to tell GotCloud the path to the input files, ${SS}
- Alternatively, gotcloud.conf could be updated to specify the full paths
--out_dirtells GotCloud where to write the output.- This could be specified in gotcloud.conf, but to allow you to use the ${OUT} to change the output location, it is specified on the command-line
This should take 1-3 minutes to run.
It should end with a line like: Processing finished in 133 secs with no errors reported
If you cancelled GotCloud part way through, just rerun your GotCloud command and it will pick up where it left off.
Inside GotCloud align, not only sequence alignment but also pre-processing of sequence data, including deduplication and base quality recalibration are performed along with quality assessment, as illustrated below.
Examining GotCloud Align Output
Let's look at the output directory:
ls ${OUT}
Quality Control Files
Let's take a look at our quality control output directory:
ls ${OUT}/QCFiles
Sample Contamination/Swap
Check for sample contamination:
- *.selfSM : Main output file containing the contamination estimate.
- Check the 'FREEMIX' column for genotype-free estimate of contamination
- 0-1 scale, the lower, the better
- If [FREEMIX] >= 0.03 and [FREELK1]-[FREELK0] is large, possible contamination
- See VerifyBamID: A guideline to interpret output files for more information
- Check the 'FREEMIX' column for genotype-free estimate of contamination
less -S ${OUT}/QCFiles/HG00551.genoCheck.selfSM
Remember, use 'q' to exit out of less
q
- Is there evidence of sample contamination?
QC Metrics
See: QPLOT: Diagnose sequencing quality for more info on how to use QPLOT results.
Let's look at some quality control metrics:
cat ${OUT}/QCFiles/HG00551.qplot.stats
- What is the mapping rate & average coverage for HG00551?
Generate a pdf of quality metrics:
Rscript ${OUT}/QCFiles/HG00551.qplot.R
Examine the PDF:
evince ${OUT}/QCFiles/HG00551.qplot.pdf&
It is ok if you see a warning message when opening evince. It should still open. If not, let me know. To close evince, just close the pdf window.
- Does the Empirical vs reported Phred score look as good as we would like?
BAM Files
Binary Sequence Alignment/Map (SAM) Format
- Maps reads to Chromosome/Position
- For a detailed explanation of the SAM/BAM format, see:
- SAM/BAM Spec: http://samtools.github.io/hts-specs/SAMv1.pdf
- Additional information I put together as I started working with SAM/BAM: SAM
Let's look at the BAMs (aligned reads that are ready for variant calling):
ls ${OUT}/bams
Let's examine at the first 5 lines of the BAM file using samtools view:
${GC}/bin/samtools view -h ${OUT}/bams/HG00551.recal.bam|head -n 5
- What are the chromosome and position of the first record in the BAM file?
Accessing BAMs by Position
BAM's are so big, what if we want to see a position part way through the file?
- samtools has an option for that.
Add a region to the view command we used above. Let's find all reads that overlap positions 36907000-36907005:
${GC}/bin/samtools view -h ${OUT}/bams/HG00551.recal.bam 22:36907000-36907005
- Just a few reads.
Let's visualize what reads in that area look like using samtools tview:
${GC}/bin/samtools tview ${OUT}/bams/HG00551.recal.bam ${SS}/ref22/human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa
- Type ‘g’
- Type 22:36907000
- Type ‘n’ to color by nucleotide
- Use the arrow keys to move around and look at the area.
Understanding the syntax:
- '.' : match to the reference on the forward strand
- ',' : match to the reference on the reverse strand
- ACGTN : mismatch to reference on the forward strand
- acgtn : mismatch to reference on the reverse strand
- Do you see anything interesting?
Other tview commands:
- Type '?' for a help screen
- Type 'q' to quit tview
Feel free to play around more and browse the BAM files.
Other tools for BAMs
We have developed a lot of tools that operate on BAM files.
See Software: BamUtil Tools for a list
- Many operations:
- diff : diff 2 BAM files
- stats: per positions statistics
- bam2Fastq : convert a BAM back to a FASTQ (how I created the fastqs for this tutorial)
- Lots of others
- Feel free to try some out
- If you have any questions, let me know, I wrote most of them and am happy to help.
Logging Off
This section is specifically for the SeqShop Workshop computers.
If you are not running during the SeqShop Workshop, please skip this section.
To logout of seqshop-server, type:
exit
And close the windows.
When done, log out of the Windows machine.