SeqShop: Analysis of Structural Variation Practical, December 2014
Introduction
Main Workshop wiki page: SeqShop: December 2014
See lecture slides for the lecture slides associated with this tutorial.
Goals of This Session
- What we want to learn
- How to prepare metadata for running GenomeSTRiP.
- How to perform variant discovery and filtering for large deletions
- How to perform genotyping for large deletions
- How to perform variant discovery and filtering from third party sites.
GenomeSTRiP
GenomeSTRiP was developed at the Broad Institute and at the McCarroll Lab at the Harvard Medical School Department of Genetics: http://www.broadinstitute.org/software/genomestrip/
If you use GenomeSTRiP for your research, please cite it:
Handsaker RE, Korn JM, Nemesh J, McCarroll SA Discovery and genotyping of genome structural polymorphism by sequencing on a population scale. Nature genetics 43, 269-276 (2011) PMID: 21317889
GenomeStrip is currently included in with the seqshop example data under the svtoolkit directory. We have added the bin/ sub-directory to add a high level pipeline that will run genomestrip in the same framework as GotCloud.
Setup in person at the SeqShop Workshop
This section is specifically for the SeqShop Workshop computers.
If you are not running during the SeqShop Workshop, please skip this section.
Login to the seqshop-server Linux Machine
This section will appear redundantly in each session. If you are already logged in or know how to log in to the server, please skip this section
- Login to the windows machine
- The username/password for the Windows machine should be written on the right-hand monitor
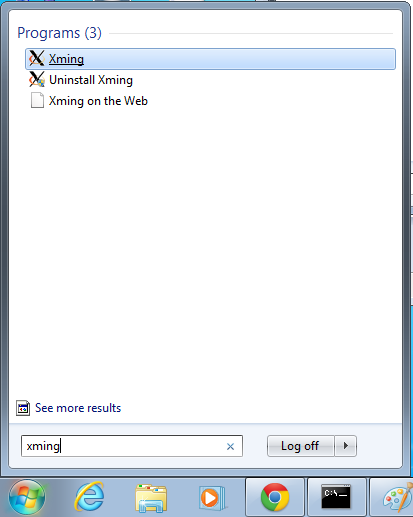
- Start xming so you can open external windows on our Linux machine
- Start->Enter "Xming" in the search and select "Xming" from the program list
- Nothing will happen, but Xming was started.
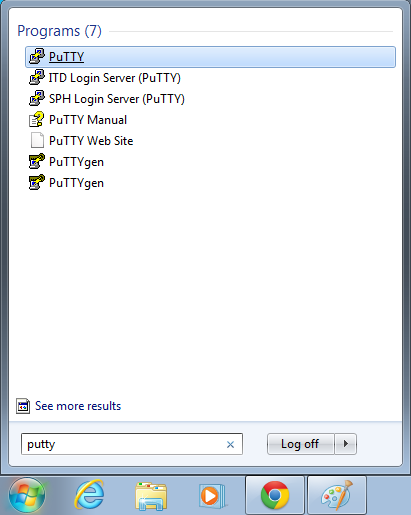
- Open putty
- Start->Enter "putty" in the search and select "PuTTY" from the program list
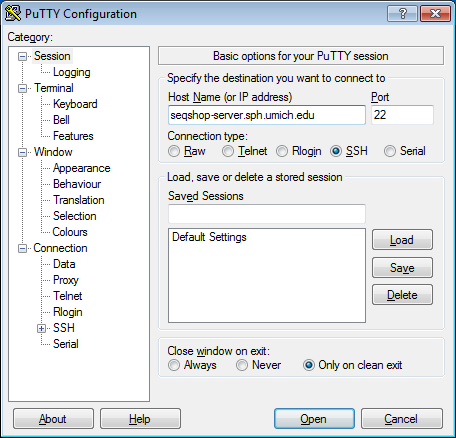
- Configure PuTTY in the PuTTY Configuration window
- Host Name:
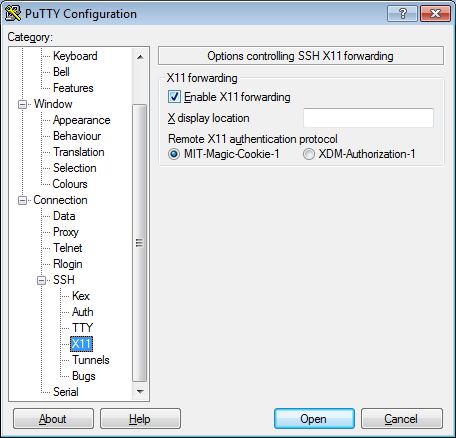
seqshop-server.sph.umich.edu - Setup to allow you to open external windows:
- In the left pannel: Connection->SSH->X11
- Add a check mark in the box next to
Enable X11 forwarding - Click
Open - If it prompts about a key, click
OK - Enter your provided username & password as provided
You should now be logged into a terminal on the seqshop-server and be able to access the test files.
- If you need another terminal, repeat from step 3.
Login to the seqshop Machine
So you can each run multiple jobs at once, we will have you run on 4 different machines within our seqshop setup.
- You can only access these machines after logging onto seqshop-server
3 users logon to:
ssh -X seqshop1
3 users logon to:
ssh -X seqshop2
2 users logon to:
ssh -X seqshop3
2 users logon to:
ssh -X seqshop4
Setup your run environment
This is the same setup you did for the previous tutorial, but you need to redo it each time you log in.
This will setup some environment variables to point you to
- GotCloud program
- Tutorial input files
- Setup an output directory
- It will leave your output directory from the previous tutorial in tact.
source /net/seqshop-server/home/mktrost/seqshop/setup.txt
- You won't see any output after running
source- It silently sets up your environment
- If you want to view the detail of the setup, type
less /net/seqshop-server/home/mktrost/seqshop/setup.txt
and press 'q' to finish.
Setup when running on your own outside of the SeqShop Workshop
This section is specifically for running on your own outside of the SeqShop Workshop.
If you are running during the SeqShop Workshop, please skip this section.
This tutorial builds on the alignment tutorial, if you have not already, please first run that tutorial: Alignment Tutorial
It also uses the bam.index file created in the SnpCall Tutorial. If you have not yet run that tutorial, please follow the directions at: GotCloud BAM Index File
Setup your run environment
Environment variables will be used throughout the tutorial.
We recommend that you setup these variables so you won't have to modify every command in the tutorial.
- Point to where you installed GotCloud
- Point to where you installed the seqshop files
- Point to where you want the output to go
- Using bash (replace the paths below with the appropriate paths):
export GC=~/seqshop/gotcloud export SS=~/seqshop/example export OUT=~/seqshop/output
- Using tcsh (replace the paths below with the appropriate paths):
setenv GC ~/seqshop/gotcloud setenv SS ~/seqshop/example setenv OUT ~/seqshop/output
Examining GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP Input files
Sequnce Alignment Files: BAM Files and Index Files
The GotCloud GenomeSTRiP structural variant caller takes the same inputs as GotCloud snpcall.
- BAMs->SVs rather than BAMs->SNPs
If you want a reminder, of what they look like, here is a link to the previous tutorial : GotCloud SnpCall Input Files
If you want to check if you still have the bam index file, run
head ${OUT}/bam.list
- View Results
HG00641 /net/seqshop-server/home/hmkang/out/bams/HG00641.recal.bam HG00640 /net/seqshop-server/home/hmkang/out/bams/HG00640.recal.bam HG00551 /net/seqshop-server/home/hmkang/out/bams/HG00551.recal.bam HG00553 /net/seqshop-server/home/hmkang/out/bams/HG00553.recal.bam HG00554 bams/HG00554.recal.bam HG00637 bams/HG00637.recal.bam HG00638 bams/HG00638.recal.bam HG00734 bams/HG00734.recal.bam HG00736 bams/HG00736.recal.bam HG00737 bams/HG00737.recal.bam
Also, make sure that you have only 62 samples (you did not append new files twice)
wc -l ${OUT}/bam.list
Your expected output is similar to this.
62 /net/seqshop-server/hmkang/out/bam.list
Reference Files
Reference files can be downloaded with GotCloud or from other sources.
- For this practical, I already downloaded them for you.
- See GotCloud: Genetic Reference and Resource Files for more information on downloading/generating reference files
Similar to SNP and Indel calling, you need
- Reference genome FASTA file
For running GenomeSTRiP, you additionally need:
- Masked FASTA file to exclude hard-to-align regions
- PloidyMap file indicating the regions of genomes with unusual ploidy (e.g. chrX, chrY)
We looked at them in previous tutorials, but you can take another look at the chromosome 22 reference files included for this tutorial:
ls ${SS}/ref22
- View Results
1000G_omni2.5.b37.sites.PASS.chr22.vcf.gz 1000G_omni2.5.b37.sites.PASS.chr22.vcf.gz.tbi 1000G.snps_indels.22.sites.bcf 1000G.snps_indels.22.sites.bcf.csi 1kg.omni.chr22.36Mb.vcf.gz 1kg.pilot_release.merged.indels.sites.hg19.chr22.vcf dbsnp.13147541variants.22.sites.bcf dbsnp.13147541variants.22.sites.bcf.csi dbsnp_135.b37.chr22.vcf.gz dbsnp_135.b37.chr22.vcf.gz.tbi dbsnp.bcf.vcf dbsnp.vcf.gz.vcf gencode.cds.22.bed.gz hapmap_3.3.b37.sites.chr22.vcf.gz hapmap_3.3.b37.sites.chr22.vcf.gz.tbi human.g1k.v37.chr22-bs.umfa human.g1k.v37.chr22.dict human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa.amb human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa.ann human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa.bwt human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa.fai human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa.pac human.g1k.v37.chr22.fa.sa human_g1k_v37.chr22.mask.100.fasta human_g1k_v37.chr22.mask.100.fasta.fai human.g1k.v37.chr22.winsize100.gc humgen_g1k_v37_ploidy.chr22.map indel.reference.txt mdust.22.bed.gz mills.208620indels.22.sites.bcf mills.208620indels.22.sites.bcf.csi mills_indels_hg19.22.sites.bcf
Parameters files required just for Structural Variation:
ls ${GC}/src/svtoolkit/conf
- View Results
genstrip_parameters.txt
GotCloud Configuration File
We will use the same configuration file we used for the GotCloud Align tutorial.
See SeqShop: Alignment: GotCloud Configuration File for more details
- Note we want to limit snpcall to just chr22 so the configuration already has
CHRS = 22(default was 1-22 & X).
For more information on configuration, see: GotCloud snpcall: Configuration File
Check out the GenomeStrip specific settings at the end of the configuration file
tail -n 5 ${SS}/gotcloud.conf
- View Results
############################## ## GenomeSTRIP ############################# GENOMESTRIP_MASK_FASTA = $(REF_DIR)/human_g1k_v37.chr22.mask.100.fasta GENOMESTRIP_PLOIDY_MAP = $(REF_DIR)/humgen_g1k_v37_ploidy.chr22.map
Before starting... a few 'why' questions..
Why use GenomeSTRiP?
- GenomeSTRiP is a mature software for detecting and genotyping large deletions (and duplications soon to be implemented). In 1000 Genomes, GenomeSTRiP was demonstrated as one of the top-performing SV caller in most evaluation metrics.
- GenomeSTRiP is a great tool to integrate across multiple structural variant calls. When multiple structural variant calls exists, all the other variants can be genotyped and filtered with GenomeSTRiP, and that is how 1000 Genomes structural variant call sets were made.
- Currently, GenomeSTRiP only allows calling large deletions, but duplicate calling pipeline is under way.
Why do we use GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP pipeline?
- The main purpose of GotCloud pipelines is to provide a pipeline for users with limited knowledge and experience with high performance computing environment.
- GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP provide a simple interface consistent to alignment, SNP, and indel calling.
- GenomeSTRiP itself also provides a straightforward pipeline to use as standalone software
- GotCloud supports a variety of cluster environment that is not currently supported by GenomeSTRiP
- GenomeSTRiP is designed based on a framework called Qscript, which provide a nice support for LSF cluster system
- GotCloud support many additional cluster environments such as MOSIX or SLURM we use locally at Michigan.
- GotCloud also provide a fault-tolerant solution for large-scale jobs.
- GotCloud automatically picks up jobs from the point where it failed. This allows easier and simpler run against potential technical glitches in the system.
Overview of GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP pipeline
GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP pipeline consists of three separate steps.
- Preprocess step : Create metadata summarizing the GC profiles, depth distribution, insert size distribution for accurate discovery and genotyping of structural variants.
- Discovery step : Perform variant discovery split by region, across all samples. Also, perform variant filtering based on expert knowledge.
- Genotyping step : Iterate discovered variants across the samples and calculate the genotype likelihood of for each possible genotype.
In addition, if one wants to genotype structural variants from other structural variant caller, there is a step available.
- Third-party Genotyping and Filtering step : Perform genotyping on the variant sites specified by an input VCF, and also perform variant filtering.
Command Line Usage of GenomeSTRiP pipeline
To see how to use GenomeSTRiP pipeline, type
perl $GC/bin/genomestrip.pl
View Results
ERROR: One of command options among --run-metadata, --run-discovery, --run-genotype, --run-thirdparty must be specified
ERROR: Missing required option, outdir
Usage:
/net/seqshop-server/home/mktrost/seqshop/gotcloud/bin/genomestrip.pl
[options]
Help Options:
-help Print out brief help message [OFF]
-man Print the full documentation in man page style [OFF]
Command options:
-run-metadata Create metadata [OFF]
-run-discovery Run variant discovery and filtering. Can run with --run-metadata together [OFF]
-run-genotype Run genotyping - requires to finish run-metadata and run-discovery [OFF]
-run-thirdparty Run genotyping and filtering of third-party sites [OFF]
Options for input/output data:
-gotcloudroot|gcroot STRGotCloud Root Directory []
-conf STR GotCloud configuration files []
-outdir STR Override's conf file's OUT_DIR. Used as the genomestrip output directory unless --out or GENOMESTRIP_OUT is set []
-list STR BAM list file containing ID and BAM path []
-out STR Output directory which stores subdirectories such as metadata/, discovery/, genotypes/, thirdparty/ unless overriden individually []
-metadata STR Output directory to store --run-metadata results. Default is [OUT]/metadata/ []
-discovery STR Output directory to store --run-discovery results. Default is [OUT]/discovery/ []
-genotype STR Output directory to store --run-genotype results. Default is [OUT]/genotype/ []
-thirdparty STR Output directory to store --run-thirdparty results. Default is [OUT]/thirdparty/ []
Advanced Options:
-tmp-dir STR temporary directory to store temporary files. Default is [OUT]/tmp []
-gs-dir STR GenomeSTRiP svtoolkit directory []
-param STR GenomeSTRIP parameter file []
-ref STR Reference FASTA file []
-mask STR Reference mask FASTA file []
-ploidy-map STR Ploidy map file []
-mosix-opt STR MOSIX options []
-region STR Region to focus on the variants []
-unit INT Number of variants to be genotyped per parallel run [100]
Additional Inputs:
-in-vcf STR Input site VCF files used for --run-genotype or --run-thirdparty. For --run-thirdparty, this argument is required. For --run-genotype, default is [OUT]/discovery/discovery.vcf []
-pass-only Genotype only PASS-filtered variants, default is OFF [OFF]
-skip-rc Skip precomputing read count [OFF]
-base-prefix STR Prefix of all files []
-bam-prefix STR Prefix of BAM files []
-ref-prefix STR Prefix of Reference FASTA files []
-no-phonehome Skip phone home functionality [OFF]
-make-base-name STR Specifies the basename for the makefile []
-verbose Specifies that additional details are to be printed out [OFF]
-dry-run Perform a dry-run that only produces Makefile but not run it [OFF]
-numjobs INT Number of jobs to concurrently run [1]
-autosomes Perform analysis only on autosomes [OFF]
Running GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP Metadata Pipeline
We first need to create metadata summarizing genome-wide statistics such as GC profiles, depth distribution, insert size distributions.
In principle, the metadata can be created from the input BAM files by running the following command
perl ${GC}/bin/genomestrip.pl --run-metadata --conf ${SS}/gotcloud.conf --numjobs 12 --base-prefix ${SS} --outdir ${OUT}
WAIT!!!!! DO NOT RUN THIS COMMAND, because it will take >1 hour to finish.
Instead, let's look what the output would have looked like.
ls ${SS}/metadata
computerc.args.list cpt depth depth.args.list depth.dat gcprofile gcprofiles.list gcprofiles.zip genome_sizes.txt isd isd.dist.args.list isd.dist.bin rccache rccache.bin rccache.bin.idx rccache.list rccache.merge spans spans.args.list spans.dat
The directory contains metadata output and other intermediate files produced by "GenomeSTRiP SVProcess" step.
See [[1]] for the details of the Preprocess step.
NOTE: You don't always have to create the metadata on your own. You can in principle use the public metadata generated for 1000G samples, under the assumption that the metadata share similar characteristics to your samples. But if you have enough computing resources, the best practice is to create metadata specifically for your sequence data.
Running GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP Discovery Pipeline
To discover large deletions from the 62 BAMs we are using for this workshop, you can run the following command
perl ${GC}/bin/genomestrip.pl --run-discovery --metadata ${SS}/metadata --conf ${SS}/gotcloud.conf --numjobs 4 --conf ${SS}/gotcloud.conf --numjobs 2 --region 22:36000000-37000000 --base-prefix ${SS} --outdir ${OUT}
${GC}/bin/genomestrip.pl -run-discoveryruns the GenomeSTRiP Discovery Pipeline--metadata ${SS}/metadatapoints to the pre-made metadata file as explained in the previous section, Running GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP Metadata Pipeline.--conf ${SS}/gotcloud.confpoints to the configuration file to use.- The configuration for this test was downloaded with the seqshop input files (same as other tutorials).
--numjobstells how many jobs to run in parallel- Depends on your system
--region 22:36000000-37000000- The sample files are just a small region of chromosome 22, so to save time, we tell the pipeline to ignore the other regions
--base_prefixtells the pipeline the prefix to append to relative paths.- The Configuration file cannot read environment variables, so we need to tell it the path to the input files, ${SS}
- Alternatively, gotcloud.conf could be updated to specify the full paths
--out_dirtells GotCloud where to write the output.- This could be specified in gotcloud.conf, but to allow you to use the ${OUT} to change the output location, it is specified on the command-line
- Based on
gotcloud.conf, the GenomeSTRiP output will go in$(OUT_DIR)/sv
This will take ~2-3 minutes to finish.
Let's see the final outputs produced.
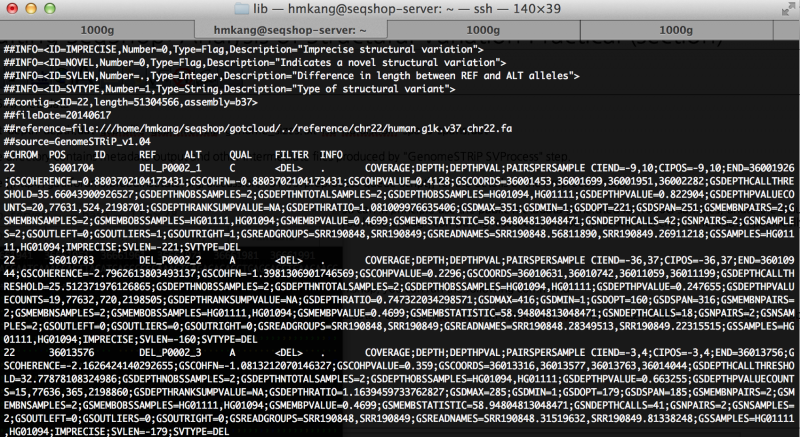
less ${OUT}/sv/discovery/discovery.vcf
You will see output file that looks like this
How many variants are filtered out?
Run the following command to see filtering statistics.
grep -v ^# $OUT/sv/discovery/discovery.vcf | cut -f 7 | sort | uniq -c
You will see the following output
7 COHERENCE;COVERAGE;DEPTH;DEPTHPVAL
18 COHERENCE;COVERAGE;DEPTH;DEPTHPVAL;PAIRSPERSAMPLE
3 COHERENCE;COVERAGE;DEPTH;PAIRSPERSAMPLE
2 COHERENCE;COVERAGE;DEPTHPVAL;PAIRSPERSAMPLE
1 COHERENCE;COVERAGE;PAIRSPERSAMPLE
3 COVERAGE
1 COVERAGE;DEPTH
67 COVERAGE;DEPTH;DEPTHPVAL
270 COVERAGE;DEPTH;DEPTHPVAL;PAIRSPERSAMPLE
2 COVERAGE;DEPTH;PAIRSPERSAMPLE
4 COVERAGE;DEPTHPVAL
4 COVERAGE;DEPTHPVAL;PAIRSPERSAMPLE
5 COVERAGE;PAIRSPERSAMPLE
What does it mean? There is no "PASS filter" variants! This is because the metadata was created from only a small fraction of genome (with very unusual distribution of depth across chr22!). If whole-genome metadata was used, the results will look more reasonable, and you will have some "PASS" variants. Trust me!
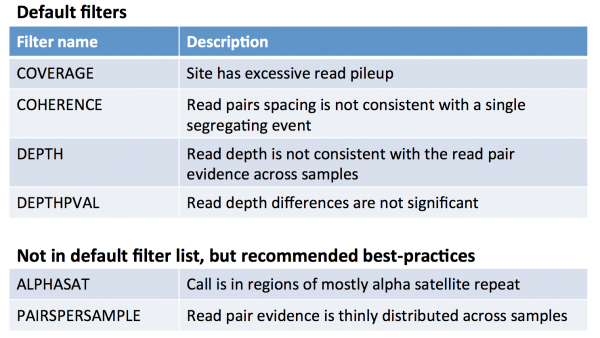
What does each filter mean?
Probably the most useful documentation of GenomeSTRiP is the powerpoint presentation available at http://www.broadinstitute.org/software/genomestrip/sites/default/files/materials/GATKWorkshop_GenomeSTRiP_tutorial_Dec2012.pdf
In slide 27, you will see the following description of the filters
Running GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP Genotyping Pipeline
The discovery pipeline only performs discovery of variant sites with filtering. You will need to iterate BAMs again to perform genotyping.
- If running on a small machine, you may want to reduce
--numjobsfrom 4 to 1.
perl ${GC}/bin/genomestrip.pl --run-genotype --metadata ${SS}/metadata --conf ${SS}/gotcloud.conf --numjobs 4 --base-prefix ${SS} --outdir ${OUT}
This will take ~3 minutes to finish.
You can check the output by running
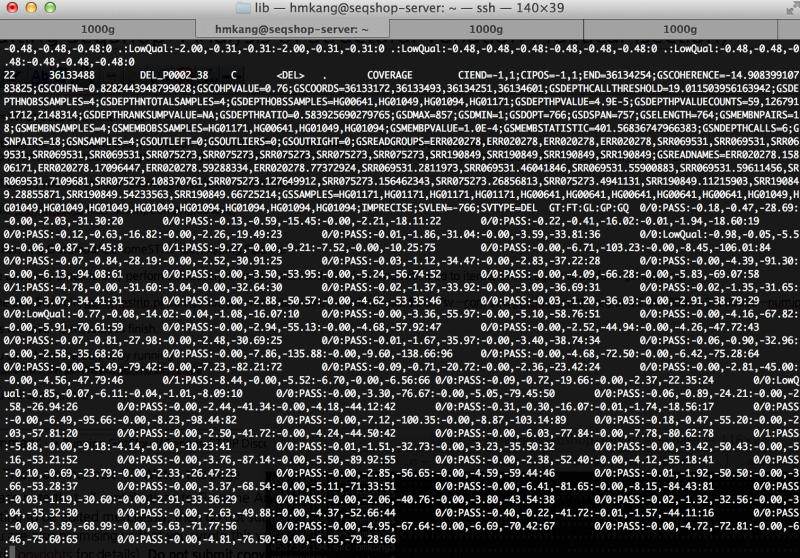
zless $OUT/sv/genotype/genotype.vcf.gz
You will see output similar to this
Running GotCloud/GenomeSTRiP 3rd-party Site Genotyping/Filtering Pipeline
You can take a 3rd-party site and genotype with GenomeSTRiP. Here we take a 1000 Genomes phase 1 sites and genotype them.
- If running on a small machine, you may want to reduce
--numjobsfrom 4 to 1.
perl ${GC}/bin/genomestrip.pl --run-thirdparty --in-vcf ${SS}/ext/1kg.phase1.chr22.36Mb.sites.vcf --metadata ${SS}/metadata --conf ${SS}/gotcloud.conf --region 22:36000000-37000000 --base-prefix ${SS} --outdir ${OUT} --numjobs 2
This will take ~1 minute to finish.
You can also check the output by running
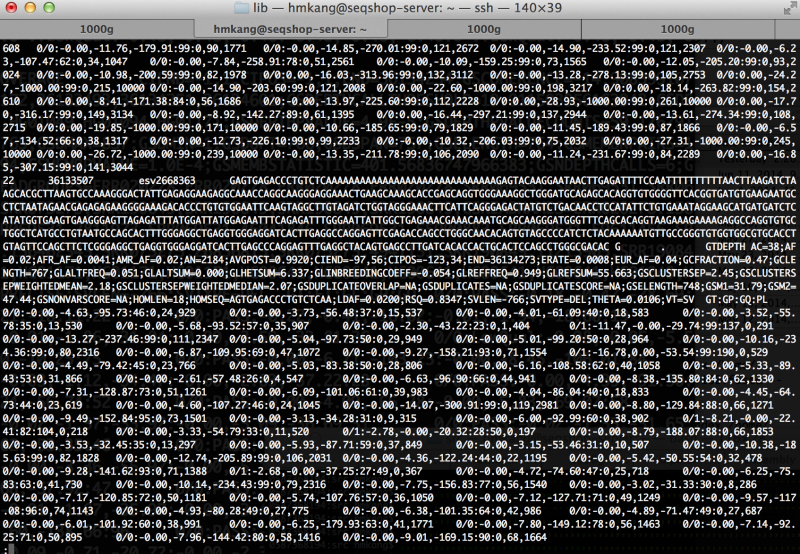
zless $OUT/sv/thirdparty/genotype.vcf.gz
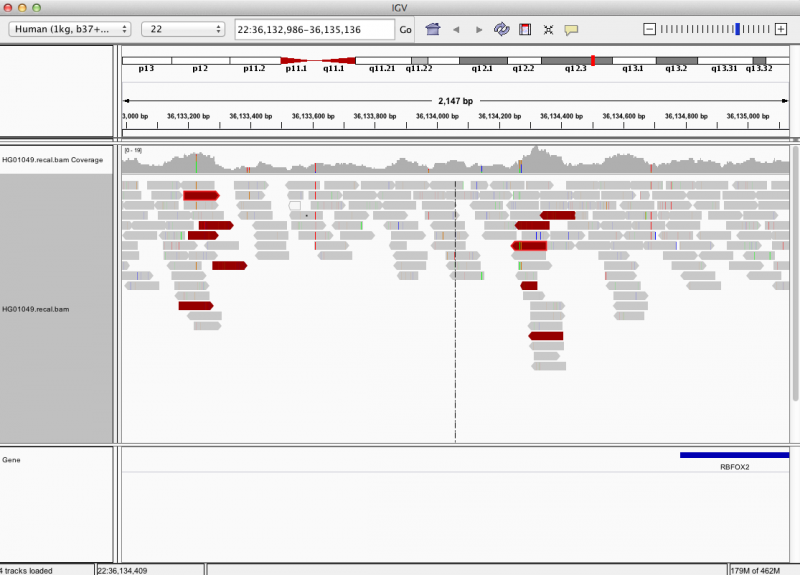
What does a real SV look like?
samtools tview does not provide a good way to visualize structural variants due to limited resolution to show large-scale variants.
IGV provides a good alternative way to visualize structural variants as shown in the xample below.
Return to Workshop Wiki Page
Return to main workshop wiki page: SeqShop: December 2014